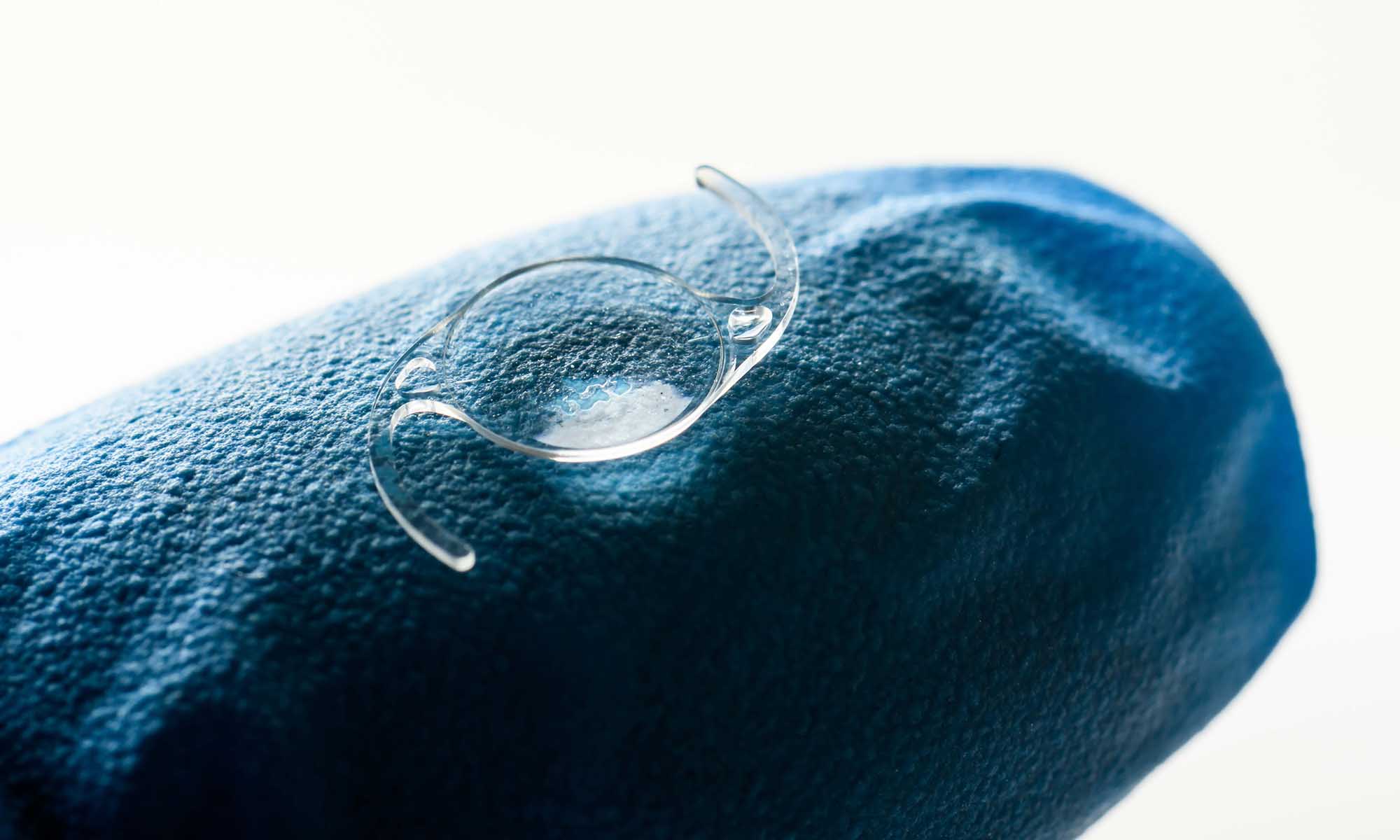
What are intraocular lenses? And how can they restore sight for patients with cataracts?
New technology is quickly improving the world’s most common form of eye surgery.

Researchers discover more efficient way to route information in quantum computers
Using qudits, Rochester scientists have solved a notoriously difficult problem involving Hilbert space, or the quantum matrix.
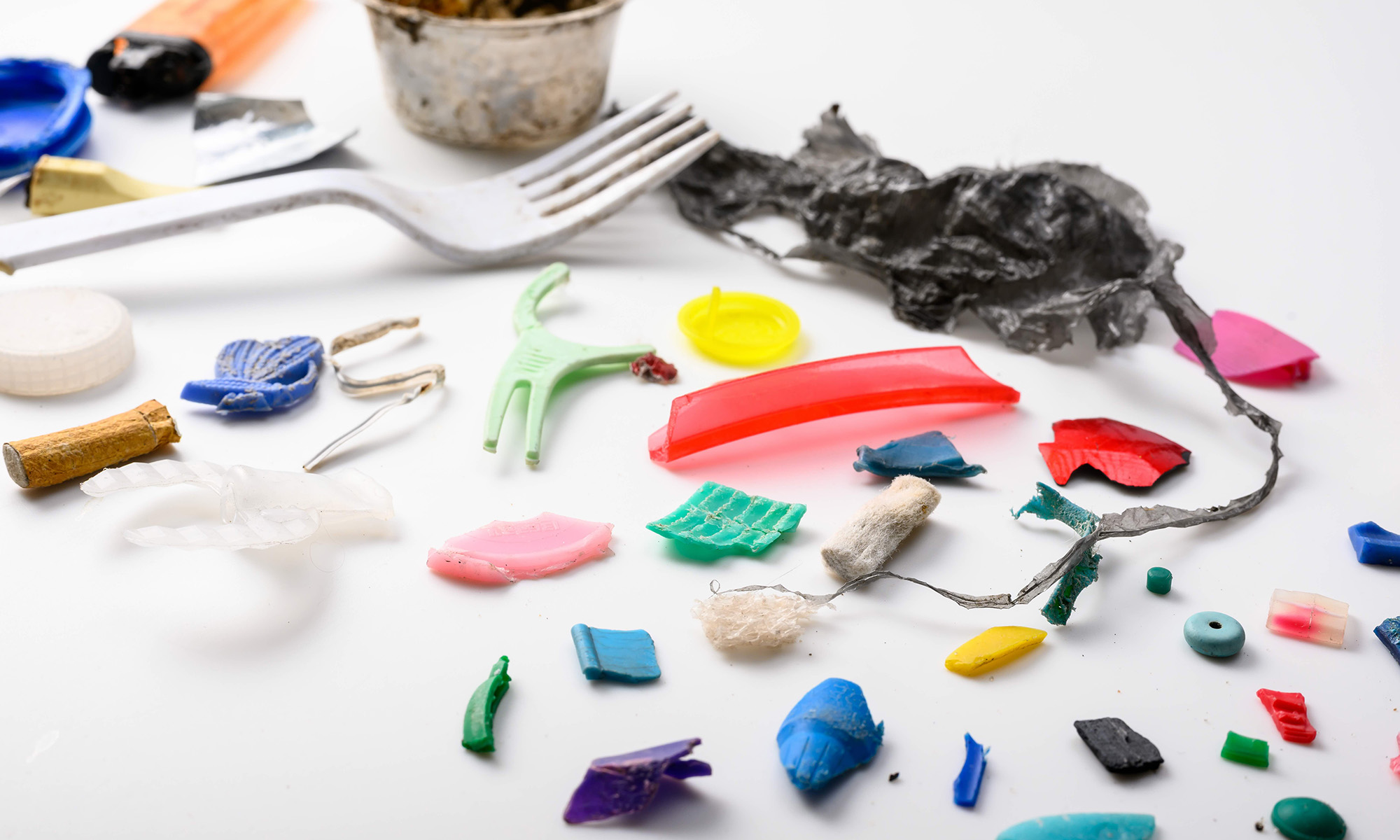

Time to throw away the plastics in your kitchen?
Rochester researchers on the growing concern of plastics exposure on human health.

The surprising way that fiber optics connects us
An optics expert explains how thin strands of glass that transmit light make modern telecommunications possible.

New method to study catalysts could lead to better batteries
A new algorithm opens the door for using artificial intelligence and machine learning to study the interactions that happen on the surface of materials.
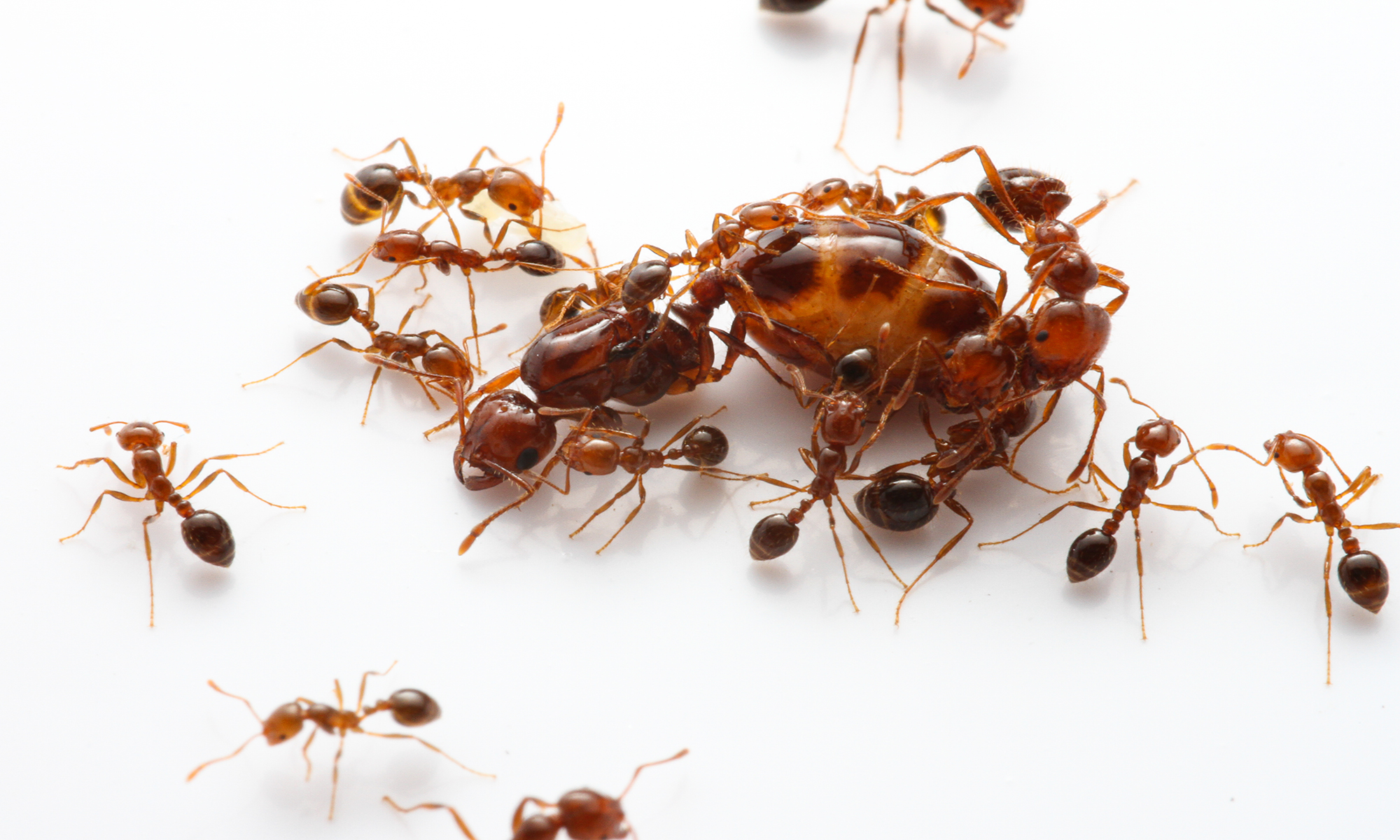

How the genetic few can sway the many
A study of fire ants reveals the surprising power of genetics in shaping social organization and group behavior.
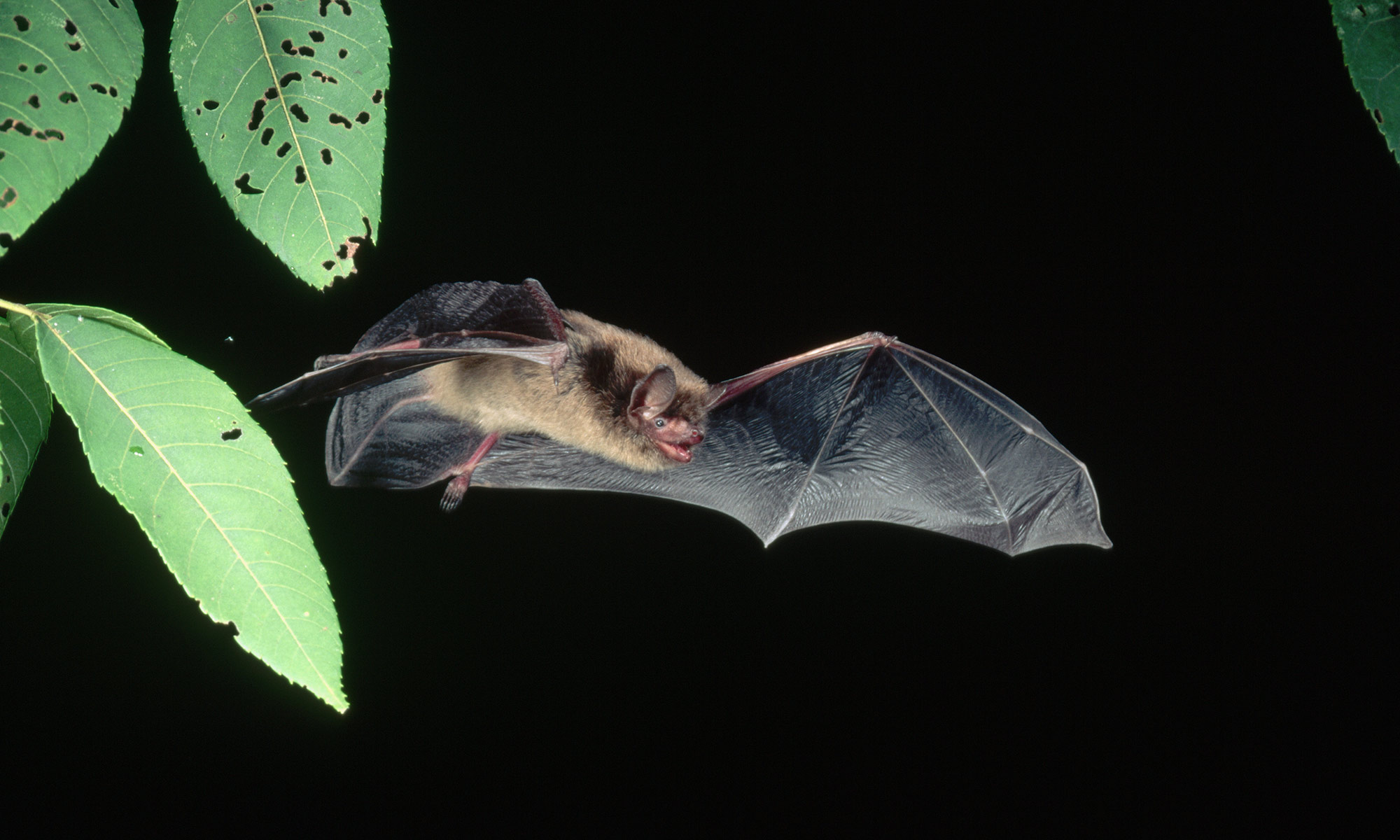

Why don’t bats get cancer?
Rochester scientists discover that long-lived bats resist cancer thanks to strong immune systems and protective genes—findings that could offer new insights into human aging and disease prevention.
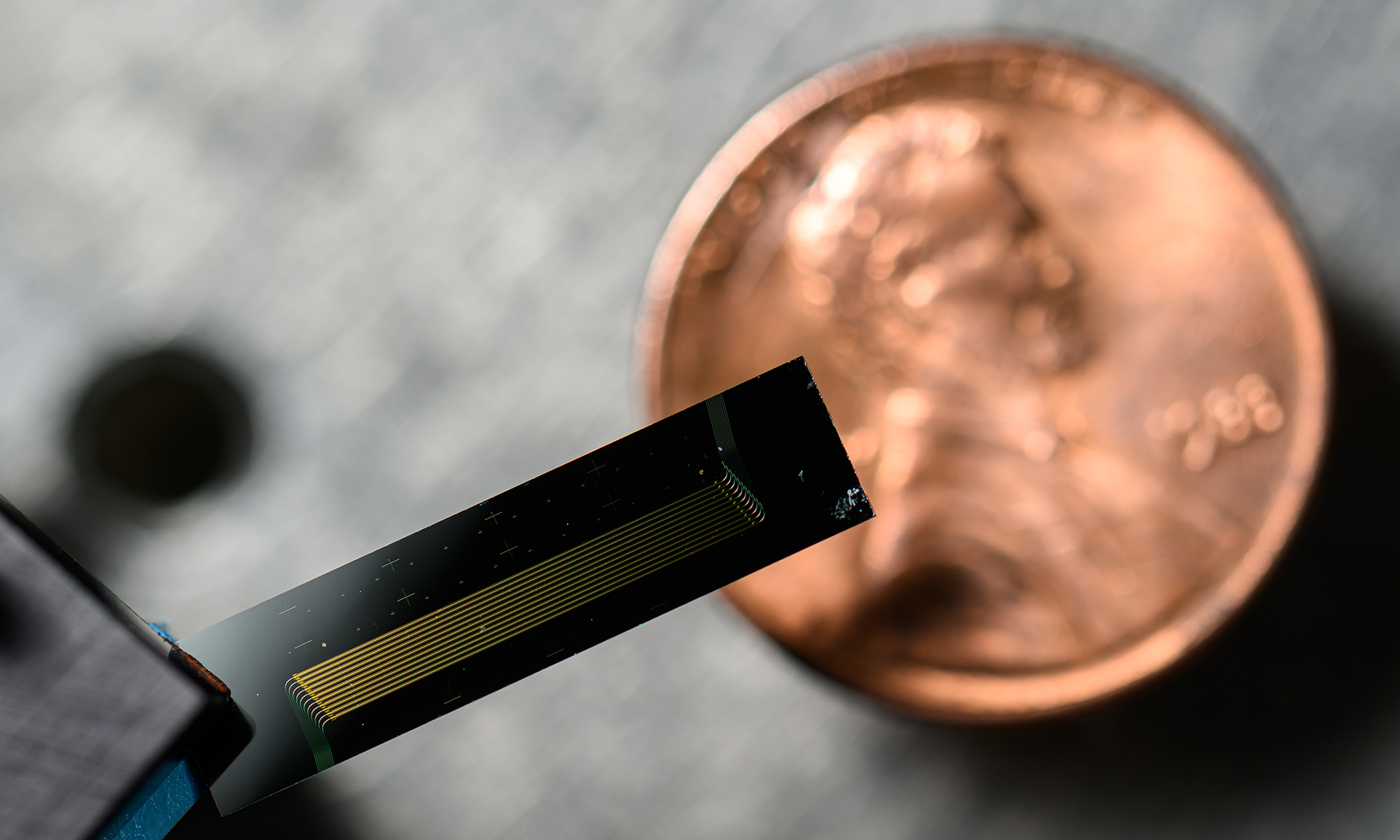
New laser smaller than a penny can measure objects at ultrafast rates
The chip-scale laser has applications ranging from guiding autonomous vehicles to detecting gravitational waves.

Pioneering physicist and optical scientist Joseph Eberly remembered
His serendipitous original foray into optics research would help advance the fields of quantum optics and optical physics.
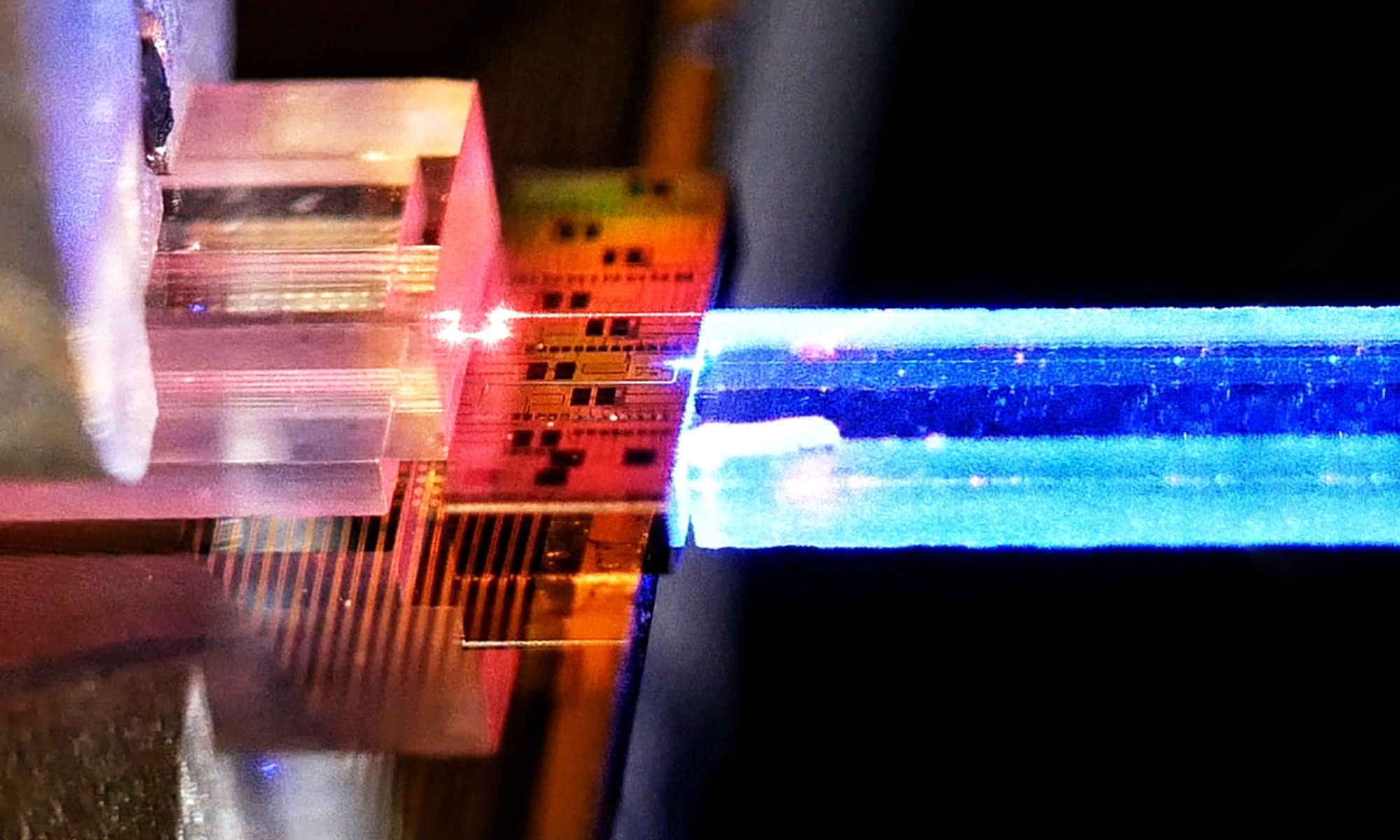
University of Rochester and RIT develop experimental quantum communications network
The Rochester Quantum Network uses single photons to transmit information over dual fiber-optic telecommunications lines.
