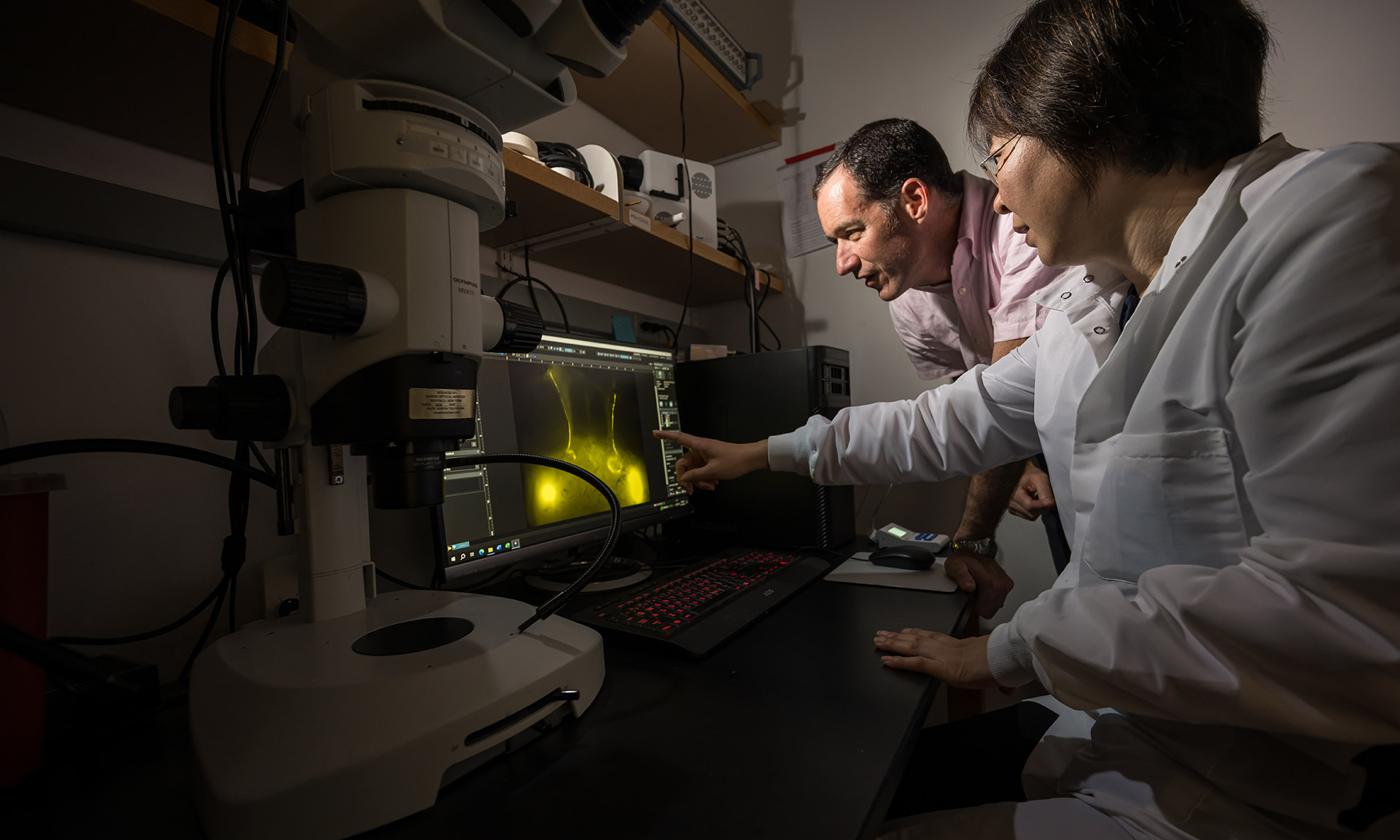

Cleaning up the aging brain
Rochester scientists are restoring the brain’s trash disposal system with a drug currently used to induce labor.
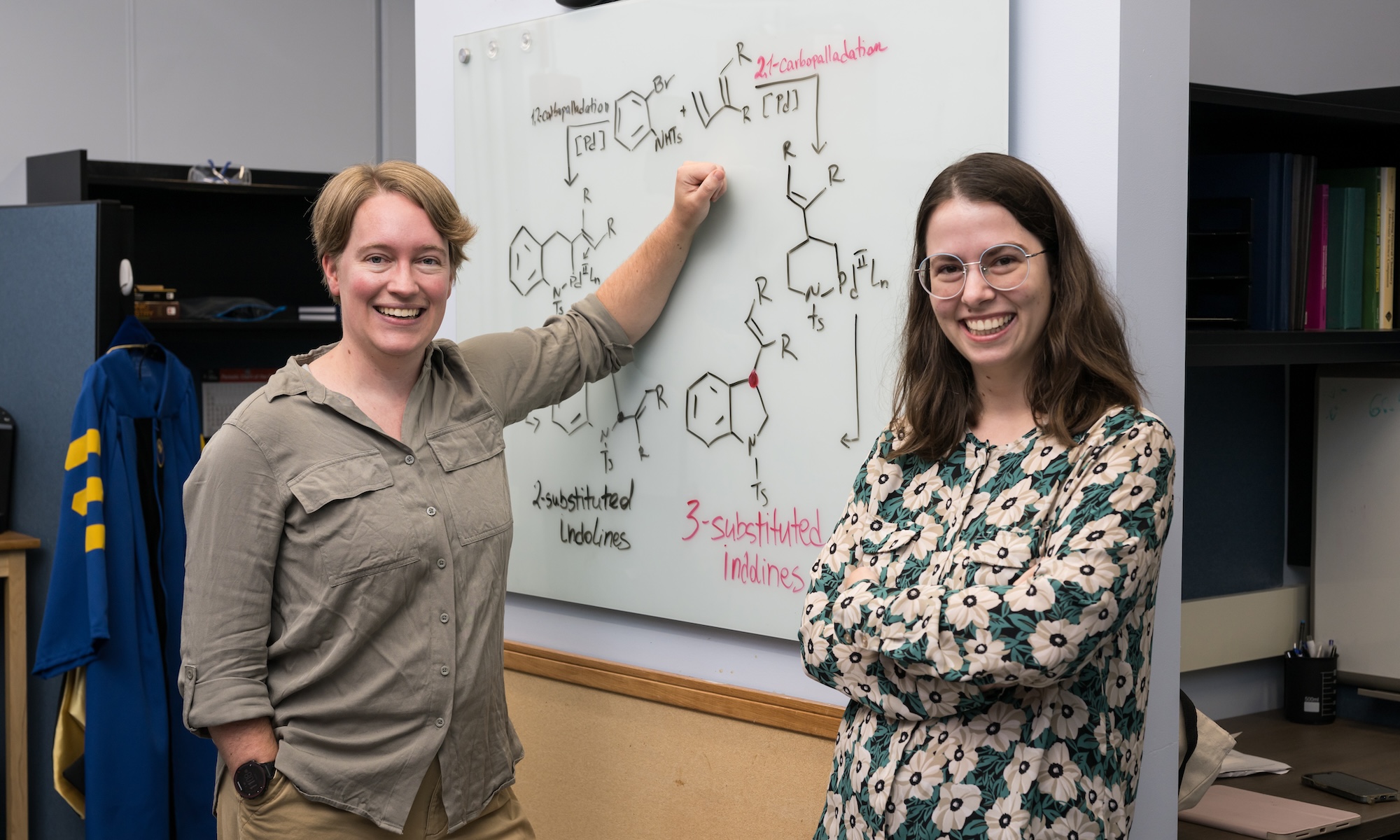
New ligand-guided technique enhances drug development
Researchers led by Shauna Paradine use chemical “helpers“ called ligands to guide reactions with extreme precision.
Who is more polarized about AI—the tech community or the general public?
An analysis of nearly 34,000 comments on Reddit provides new insights about perceptions of AI after ChatGPT’s launch.

Is a gamma-ray laser possible?
Federal funding will allow Rochester scientists and their European collaborators to study the feasibility of coherent light sources beyond x-rays.
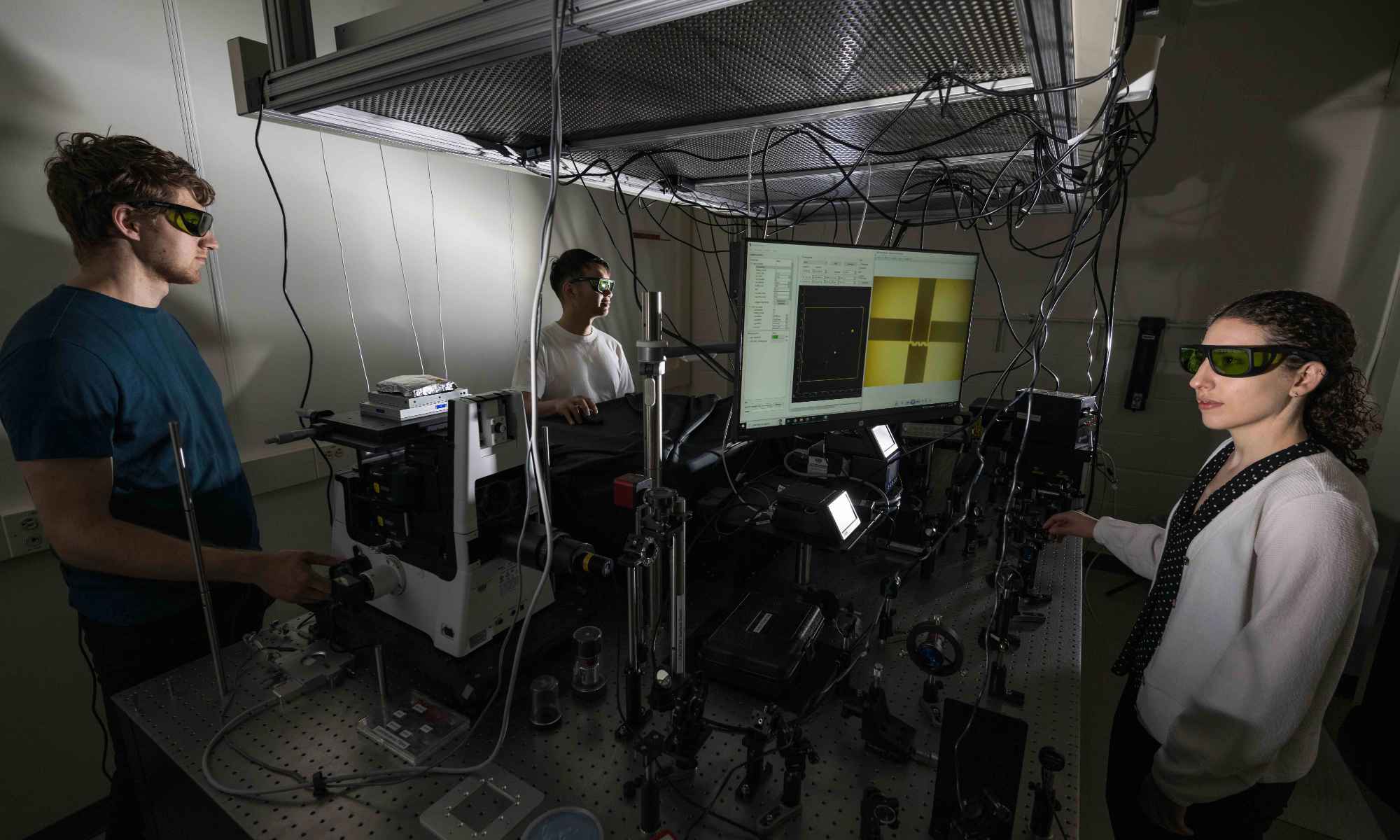
New technique pinpoints nanoscale ‘hot spots’ in electronics to improve their longevity
Rochester engineers have developed a way to spot tiny, overheated components that cause electronics’ performance to degrade.

In the hunt for a second Earth, look to small planets
The recommendation is based on new research from Rochester scientists about the role of streaming instability in forming moons and planets.
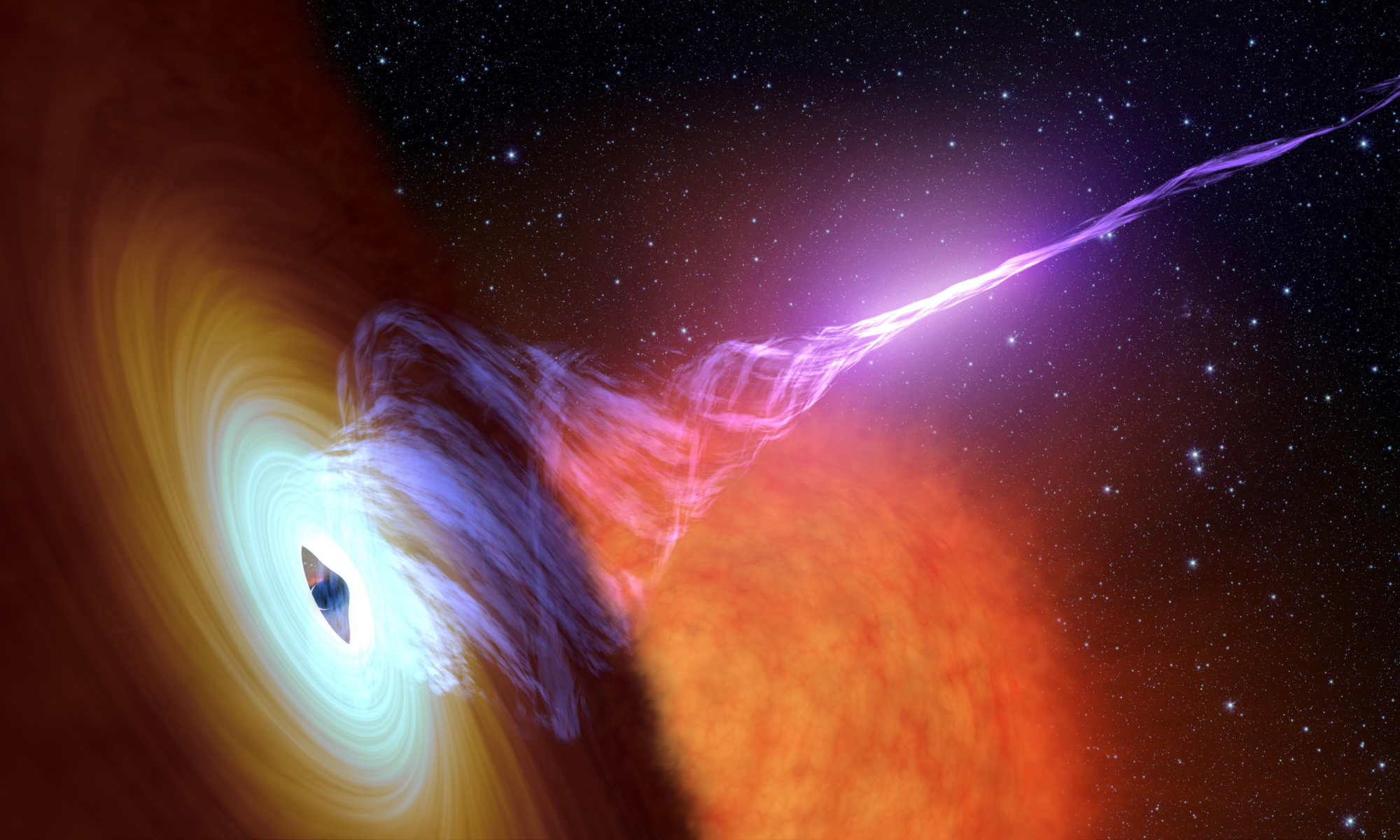

Pair plasmas found in deep space can now be generated in the lab
An international team of scientists has developed a novel way to experimentally produce plasma ‘fireballs’ on Earth.
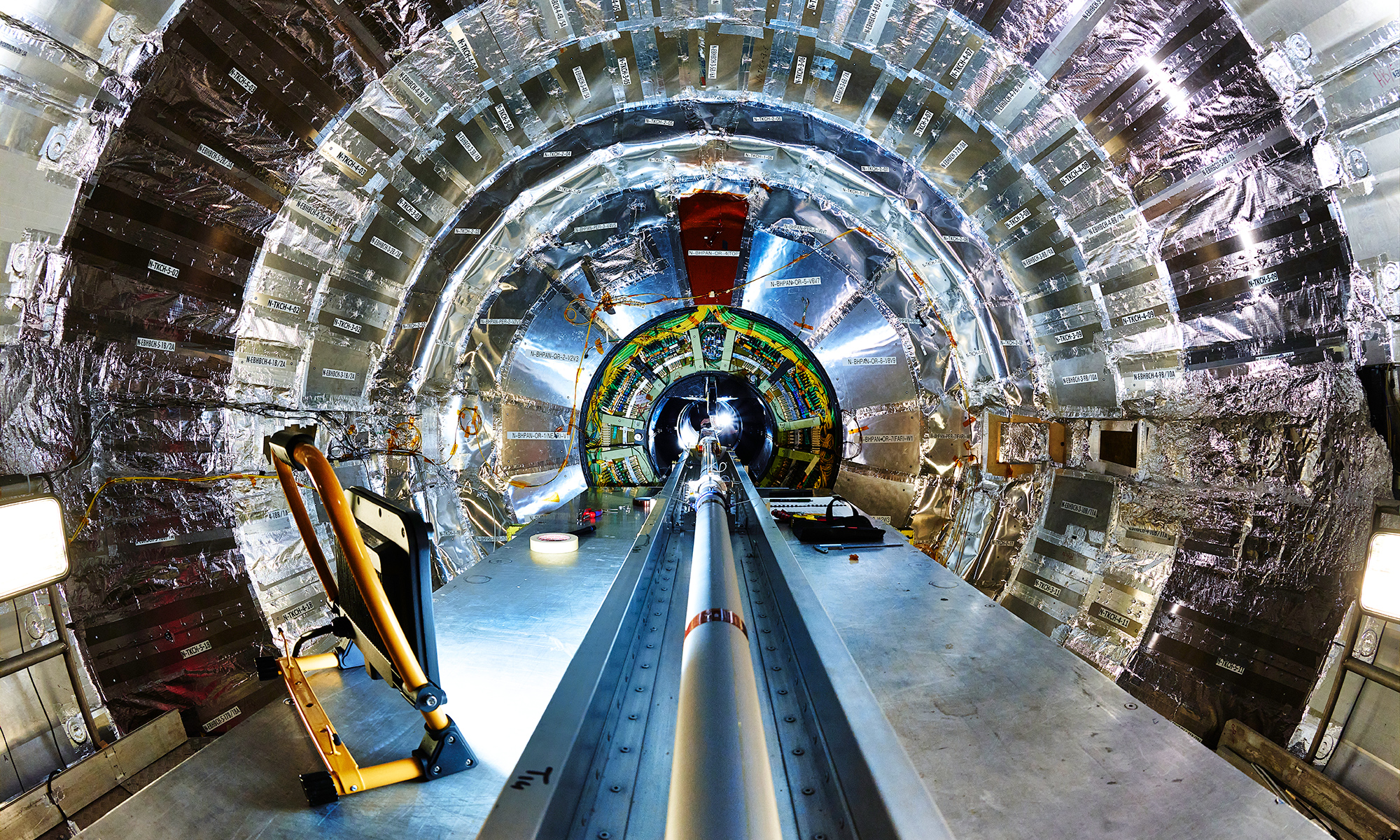

Rochester physicists find ‘spooky action at a distance’ at CERN
The researchers have confirmed that quantum entanglement persists between top quarks, the heaviest known fundamental particles.
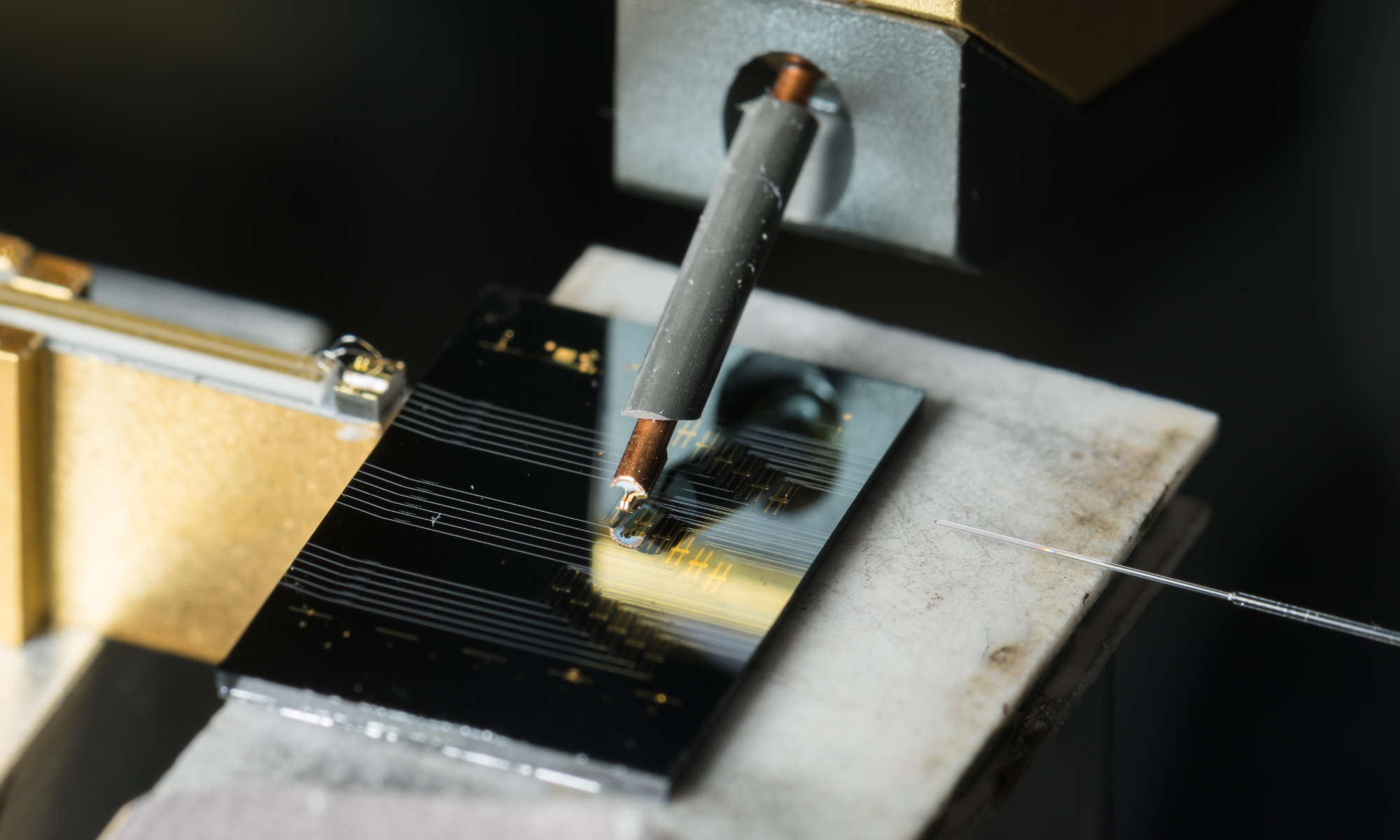

Streamlined microcomb design provides control with the flip of a switch
Microcomb lasers developed at the University of Rochester offer a new path for developing frequency comb generators at a microchip scale.
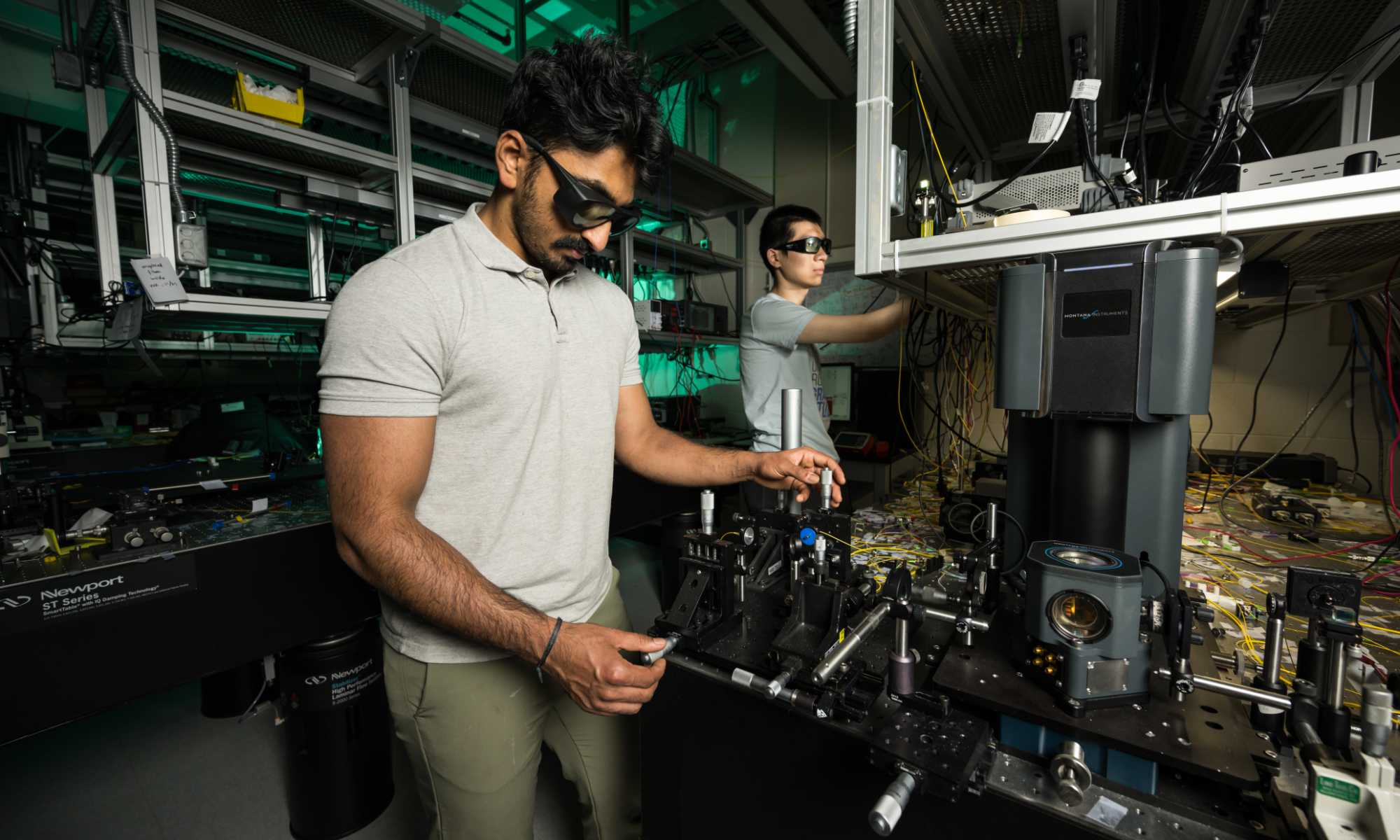

New surface acoustic wave techniques could lead to surfing a quantum internet
Researchers have developed new methods to couple light to sound waves that glide on surfaces.
