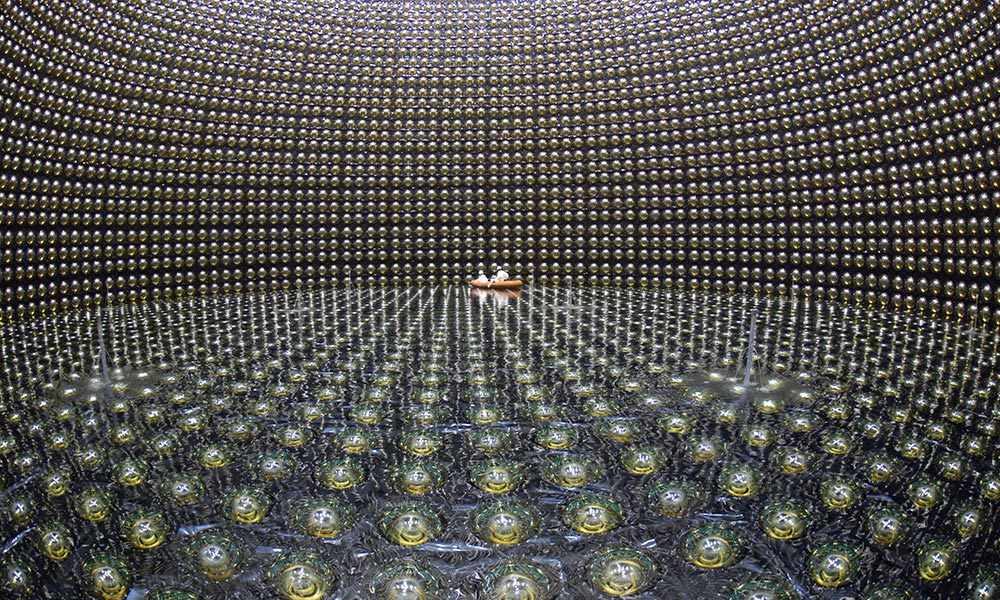
Why neutrinos ‘matter’ in the early universe
When the highly anticipated findings from the Japan-based T2K neutrino experiment were finally presented at the International Conference on High Energy Physics this month, it was Rochester graduate student Konosuke (Ko) Iwamoto who updated the physics world on the puzzle behind the imbalance between matter and antimatter.
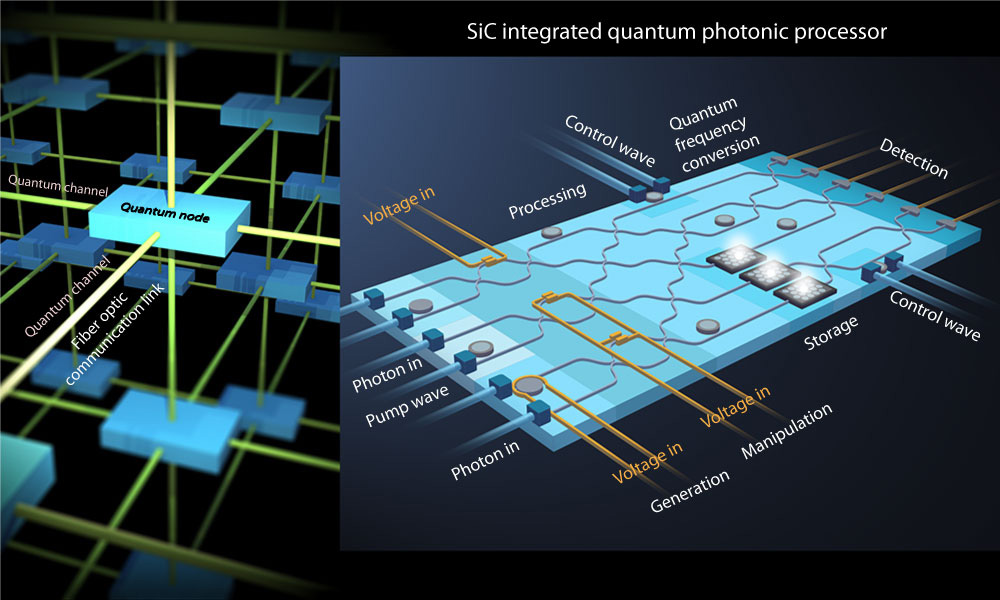
$2 million to add efficiency to integrated quantum photonics
Rochester researchers working on the next generation of quantum information processing have received a $2 million boost from the National Science Foundation.
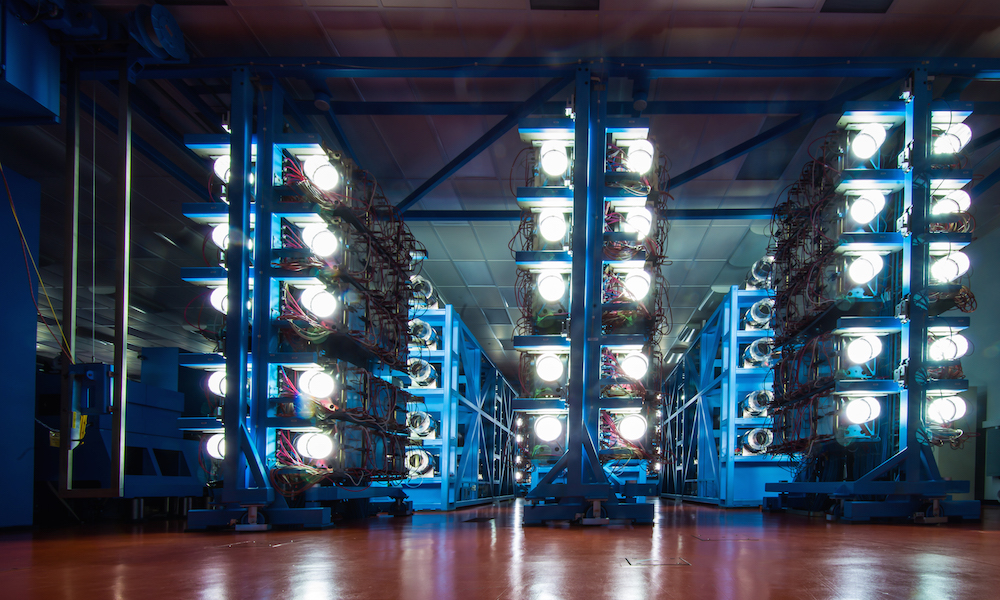

Fusion for energy: significant progress, major challenges
In a review of the state of the research in this field, Rochester physicist Riccardo Betti concludes the goal of realizing abundant, clean energy from inertial confinement fusion remains elusive, despite recent significant progress.

Making the case for life on other planets
How can we calculate the likelihood of technological civilizations having existed on other planets? That’s a question Adam Frank, professor of astronomy, considers in an essay, “Yes, There Have Been Aliens,” published in the New York Times.
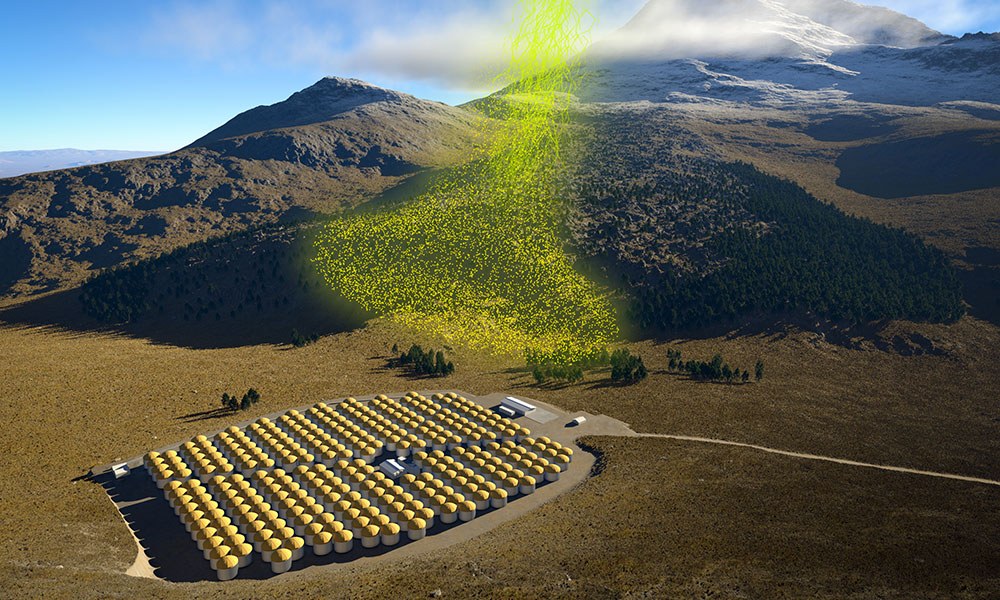

Catching some gamma rays in central Mexico
Physicist Segev BenZvi and scientists at an ambitious observatory are using simple but groundbreaking tools understand the workings of cosmic and gamma rays in the Earth’s atmosphere while also contributing to the search for dark matter.

What makes America (and civilization) great
Astronomy professor Adam Frank traces the “line from [Ellis] Chesbrough’s audacious plan to make Chicago a clean, functioning city 150 years ago and the invisible infrastructures hiding behind your cell phone” today. / NPR.org
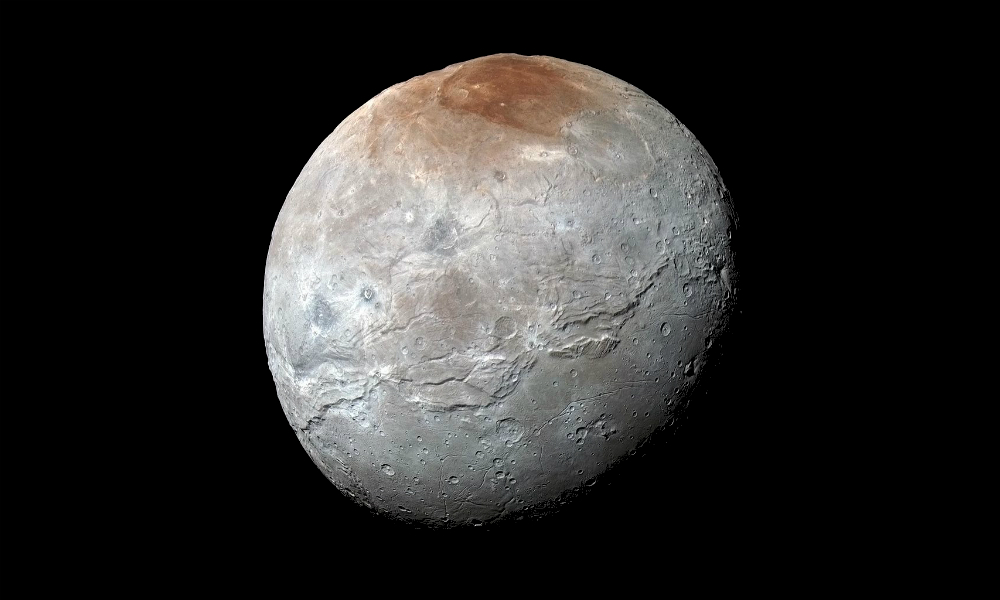

Close encounters of a tidal kind could lead to cracks on icy moons
Until now, it was thought the cracks on icy moons such as Pluto’s Charon were the result of processes like plate tectonics. But new computer models suggest that the pull exerted by another object might have been the cause.
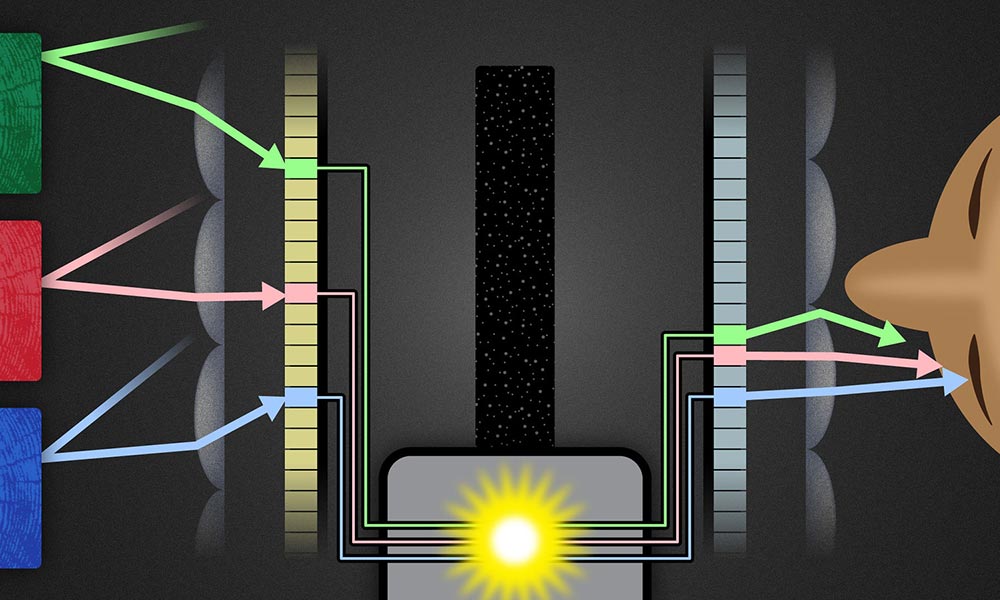
A digital ‘Rochester Cloak’ to fit all sizes
Using the same mathematical framework as the Rochester Cloak, researchers have been able to use flat screen displays to extend the range of angles that can be hidden from view. Their method lays out how cloaks of arbitrary shapes, that work from multiple viewpoints, may be practically realized in the near future using commercially available digital devices.
Researchers demonstrate record optical nonlinearity
A team led by Robert Boyd has demonstrated that the transparent, electrical conductor indium tin oxide can result in up to 100 times greater nonlinearity than other known materials, a potential ‘game changer’ for photonics applications.

Can big data resolve the human condition?
The Kavli HUMAN Project holds great promise for putting big data to the test. But as astronomy professor Adam Frank argue, “with great promise comes great responsibility.” / NPR
