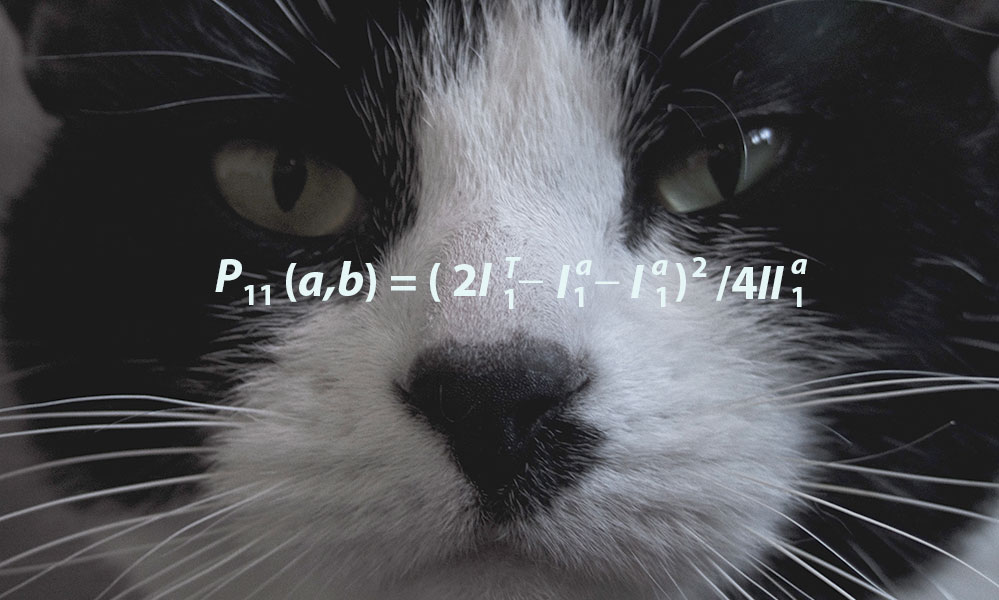
Science & Technology
A digital ‘Rochester Cloak’ to fit all sizes
May 19, 2016
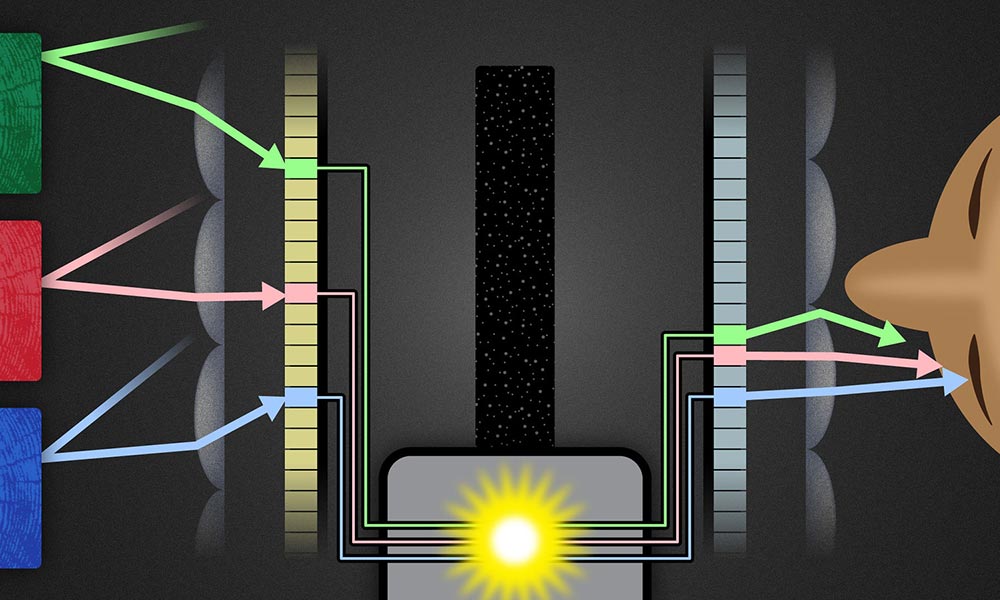
Using the same mathematical framework as the Rochester Cloak, researchers have been able to use flat screen displays to extend the range of angles that can be hidden from view. Their method lays out how cloaks of arbitrary shapes, that work from multiple viewpoints, may be practically realized in the near future using commercially available digital devices.