Science & Technology
Enigma Machine takes a quantum leap
September 6, 2016
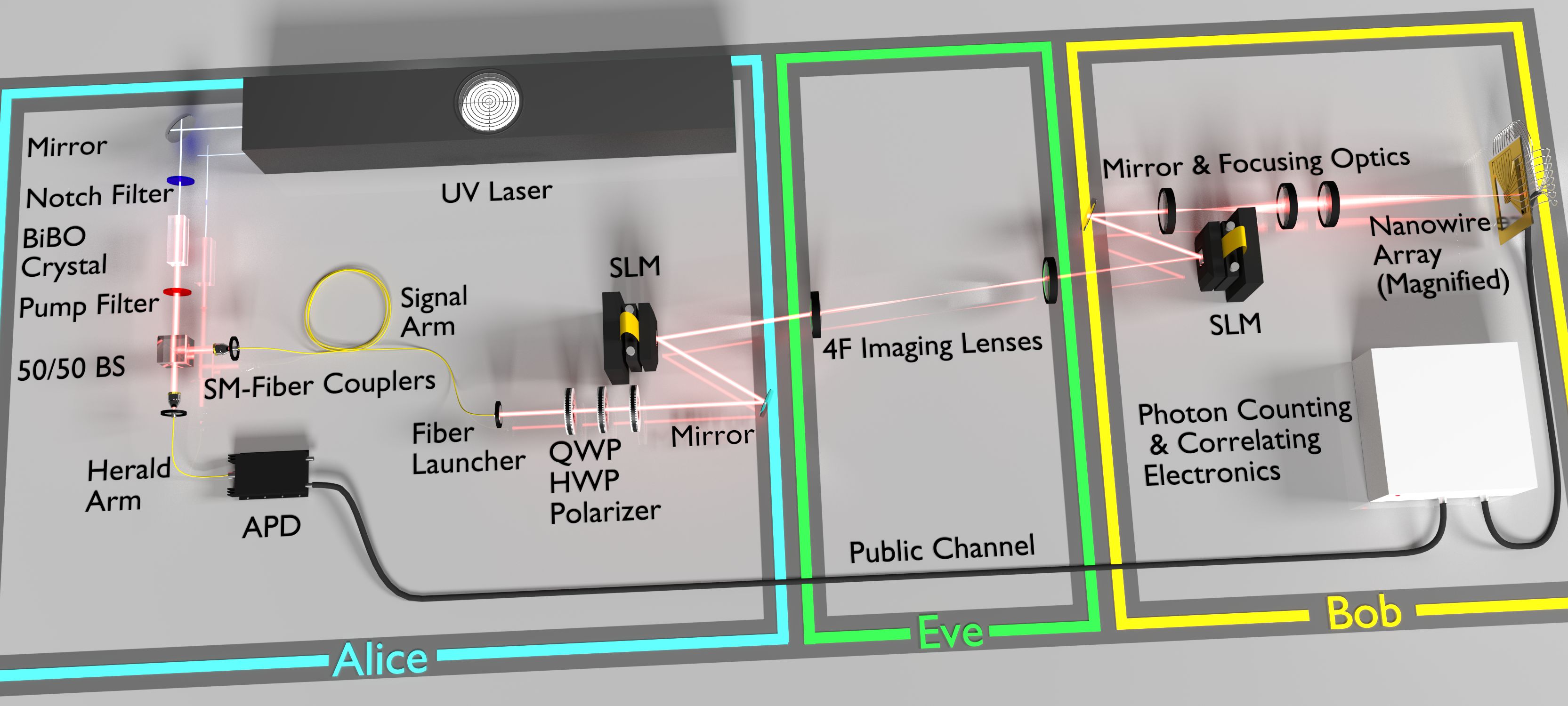
Researchers have developed a "quantum enigma machine" to improve on data encryption. The device manipulates photons to create an unbreakable encrypted message with a key that’s far shorter than the message—the first time that has ever been done.








