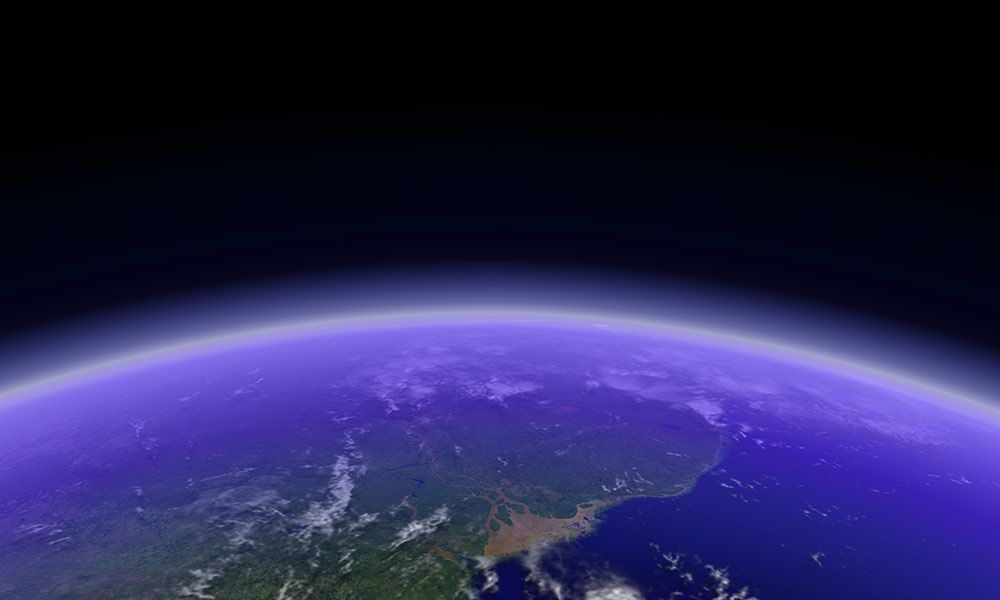

Ancient ozone levels provide a glimpse into future effects of climate change
A computer model developed at Rochester, and used to compare model data to analysis on 100,000-year-old Greenland ice cores, has shown a surprising result.
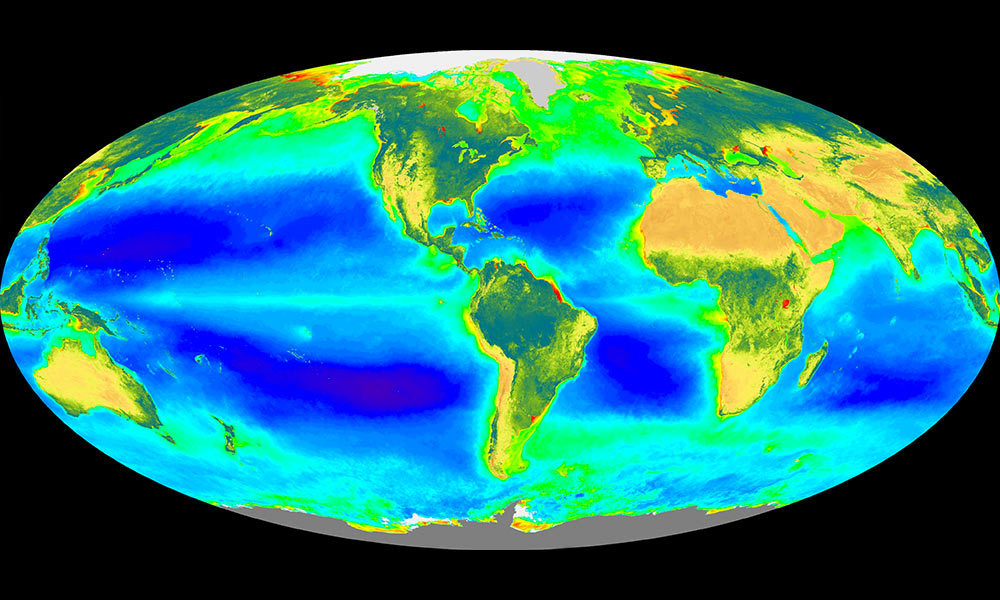
Using data science to understand global climate systems
Climate scientists and computer scientists are working together to understand what drives the global climate system—from deep in the ocean to high in the sky.
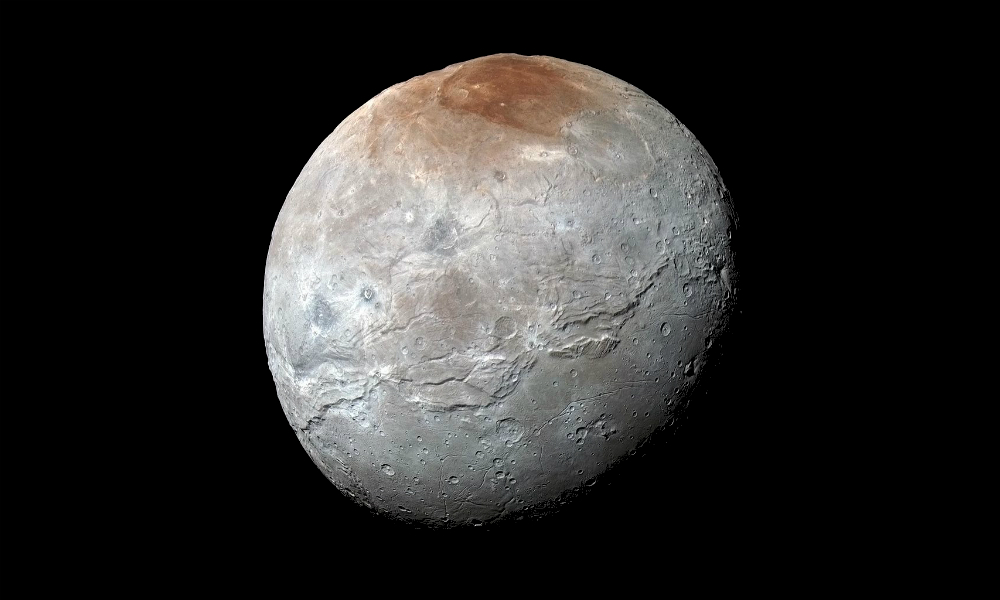

Close encounters of a tidal kind could lead to cracks on icy moons
Until now, it was thought the cracks on icy moons such as Pluto’s Charon were the result of processes like plate tectonics. But new computer models suggest that the pull exerted by another object might have been the cause.

A new way to determine the age of stars?
Rochester researchers have developed a new conceptual framework for understanding how stars similar to our Sun evolve. Their framework helps explain how the rotation of stars, their emission of x-rays, and the intensity of their stellar winds vary with time. According to Eric Blackman, professor of physics and astronomy, the work could also “ultimately help to determine the age of stars more precisely than is currently possible.”
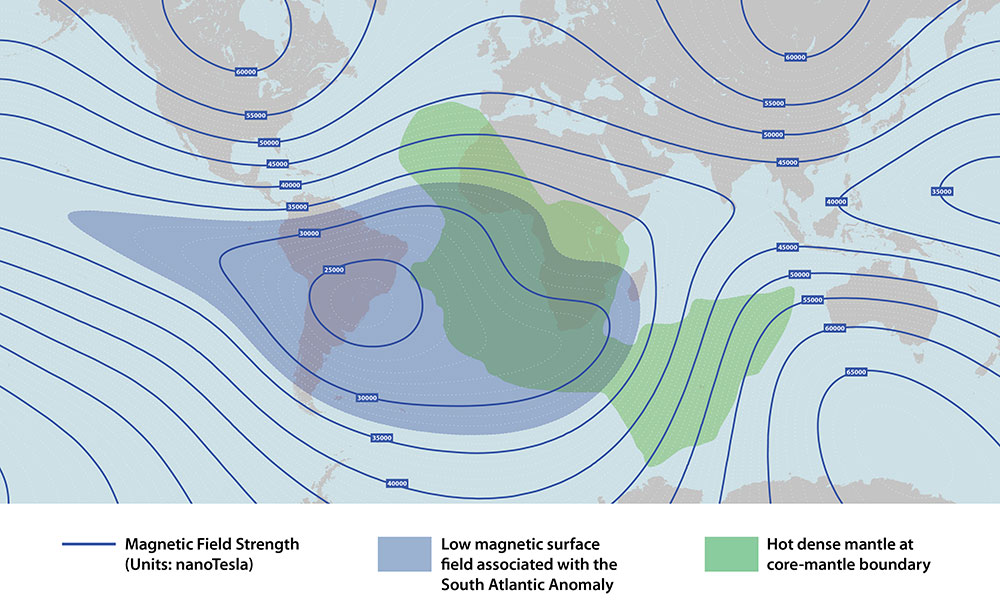
First measurements taken of South Africa’s iron age magnetic field history
Combined with the current weakening of Earth’s magnetic field, the data suggest that the region of Earth’s core beneath southern Africa may play a special role in reversals of the planet’s magnetic poles.

Sustainability, astrobiology combine to illuminate future of Earth’s technological civilization
How long can a technological civilization last? Will human-caused climate change or species extinctions threaten its collapse or can industrial development continue without restrictions? In a new paper, two astrophysicists argue that these questions may soon be resolvable scientifically.
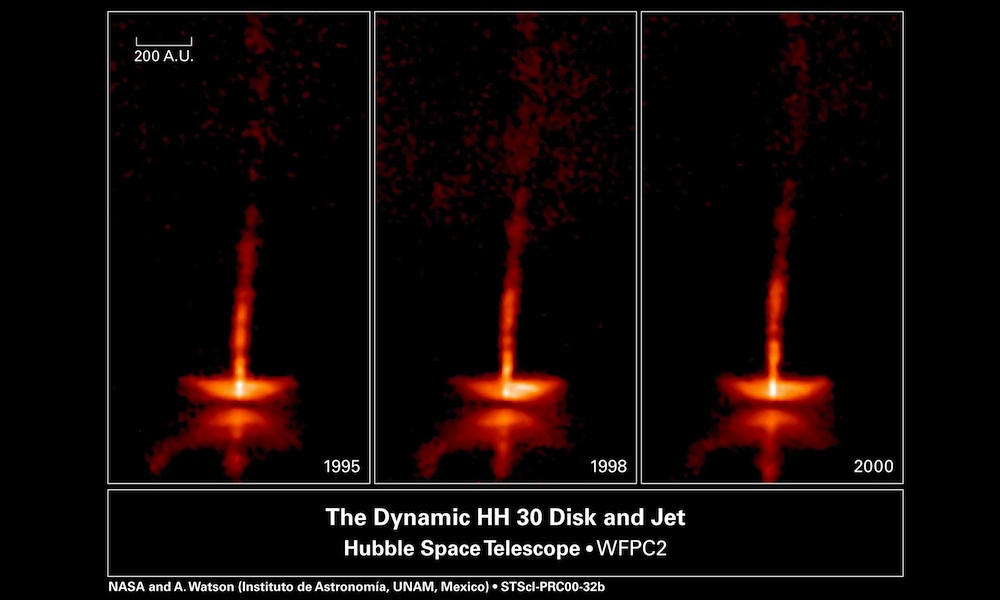
Experiment on earth demonstrates effect observed in space
Streaming jets of high-speed matter produce some of the most stunning objects seen in space. an experiment by French and American researchers using extremely high-powered lasers offers experimental verification of one proposed mechanism for creating them.

Scientist named American Physical Society Fellow
Suxing Hu, senior scientist in the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE)’s theory division, is recognized for his work in attosecond physics.
