Science & Technology
Streamlined microcomb design provides control with the flip of a switch
May 22, 2024
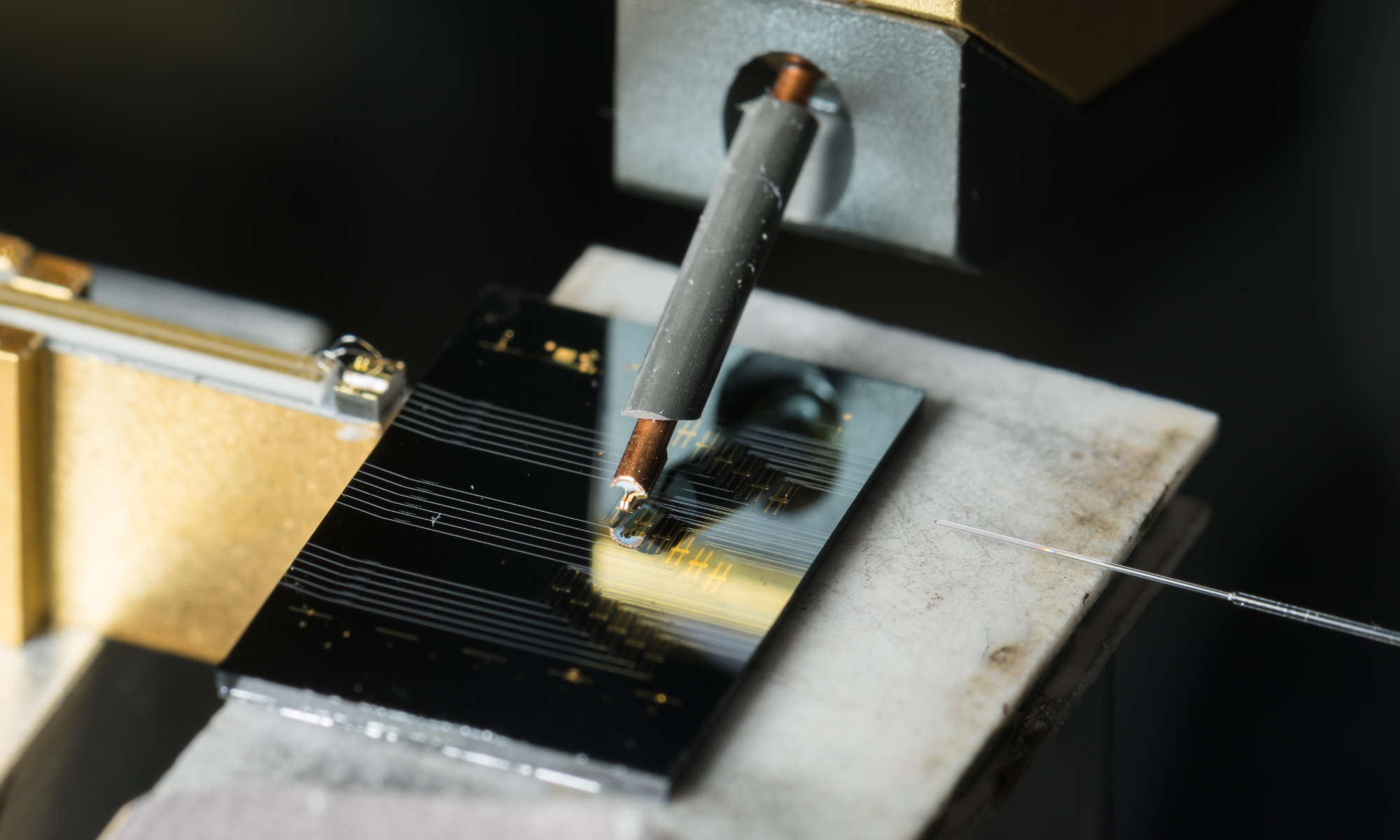
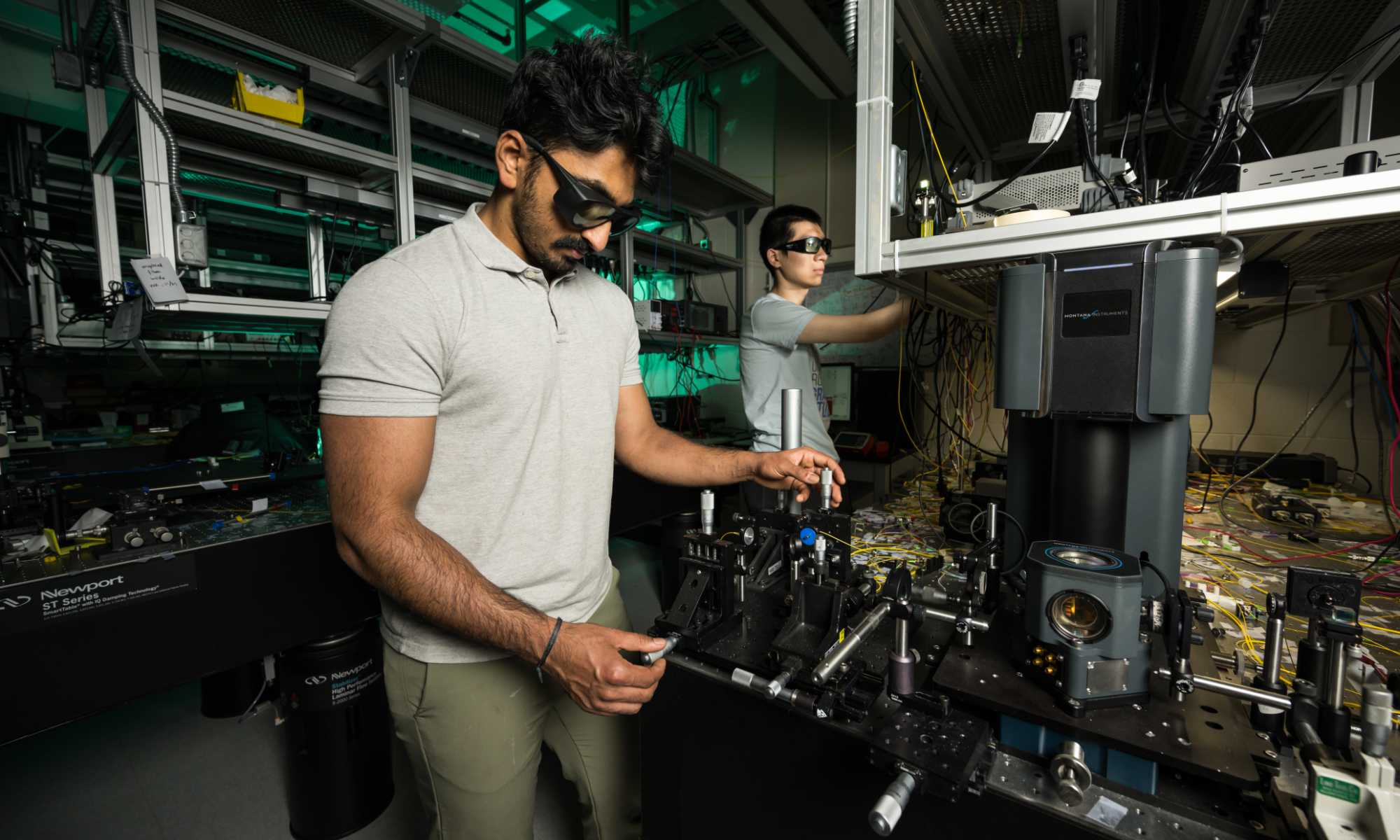
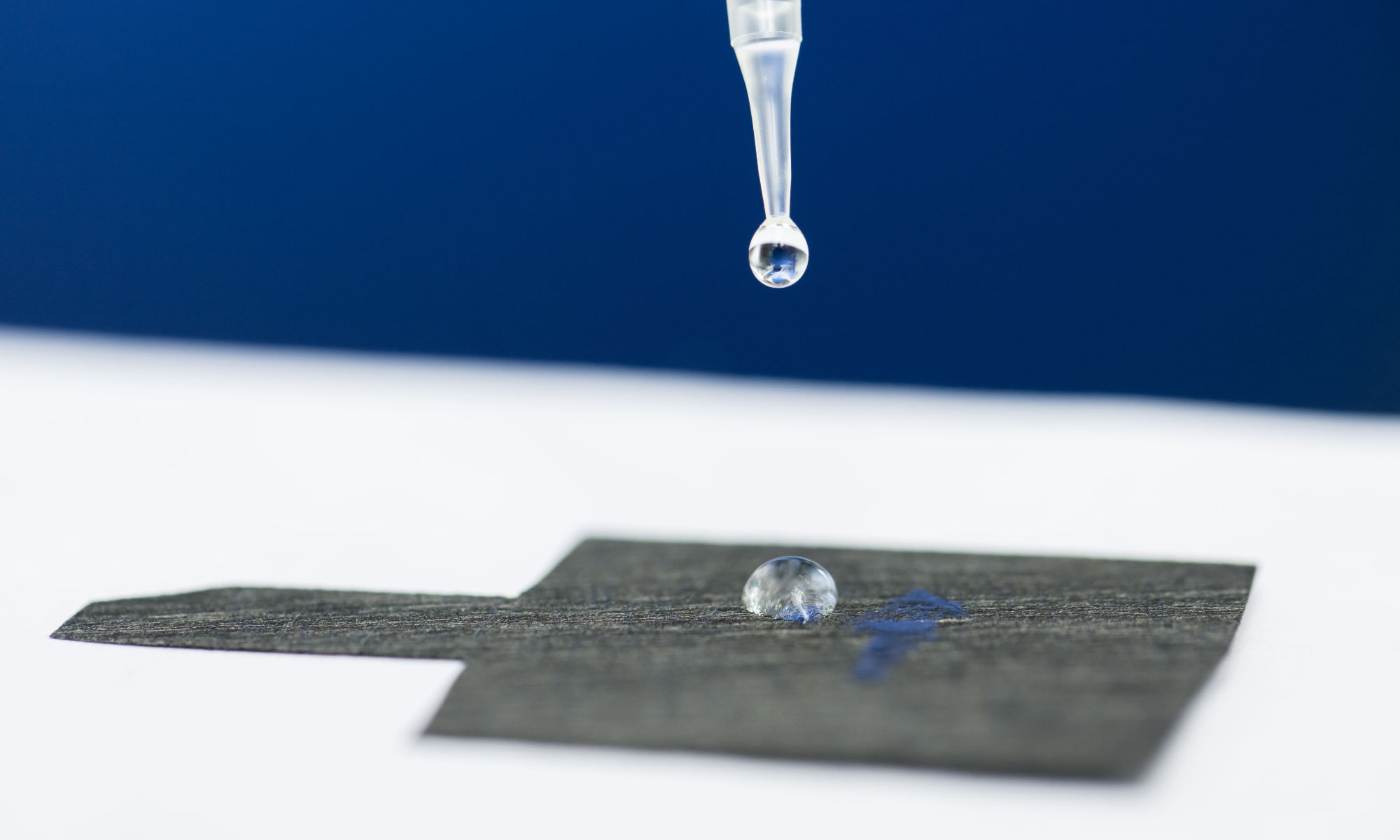
Microcomb lasers developed at the University of Rochester offer a new path for developing frequency comb generators at a microchip scale.