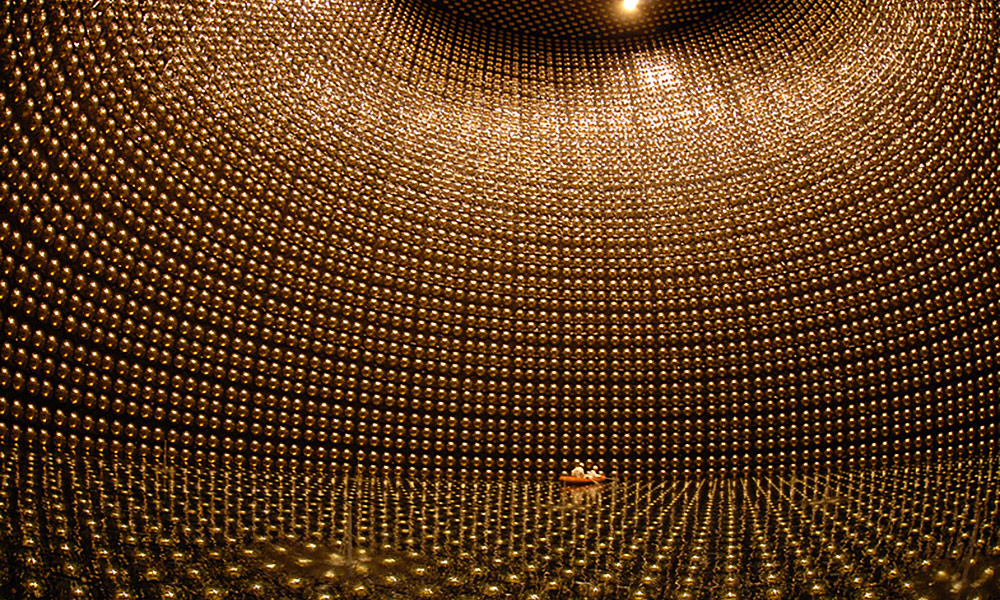
Why is the universe made up almost exclusively of matter? Neutrinos may hold the key
Experiments conducted in a mine in Japan may hold clues to explain why the matter than makes up the universe escaped annihilation by anti-matter during the Big Bang.
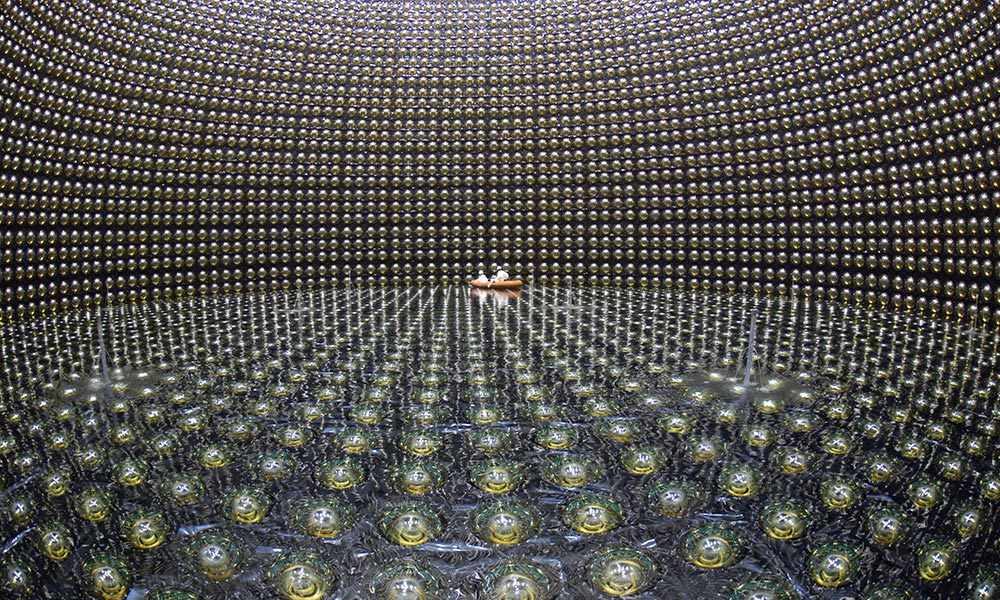
Why neutrinos ‘matter’ in the early universe
When the highly anticipated findings from the Japan-based T2K neutrino experiment were finally presented at the International Conference on High Energy Physics this month, it was Rochester graduate student Konosuke (Ko) Iwamoto who updated the physics world on the puzzle behind the imbalance between matter and antimatter.

Rochester team among those awarded $3 million Breakthrough Prize for work with neutrinos
A team led by professors Steven Manly and Kevin McFarland was honored “for the fundamental discovery of neutrino oscillations, revealing a new frontier beyond, and possibly far beyond, the standard model of particle physics.”
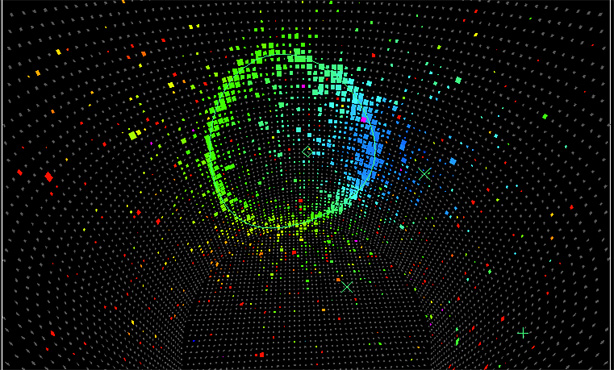
New Type of Neutrino Oscillation Confirmed
The new finding could help explore a fundamental question of science – why is the universe made up almost exclusively of matter, when matter and antimatter were created in equal amounts in the Big Bang?
