Can a planet have a mind of its own?
Adam Frank, the Helen F. and Fred H. Gowen Professor of Physics and Astronomy, asks, if a planet with life has a life of its own, can it also have a mind of its own?

Moons may yield clues to what makes planets habitable
In the search for Earth-like planets, University of Rochester scientist Miki Nakajima turns to computer simulations of moon formations.

Rochester scientists reveal the limits of machine learning for hydrogen models
Research from the Laboratory for Laser Energetics paves the way for more accurate computer models, which are needed to understand the interior of planets and the physical properties of nuclear fusion.
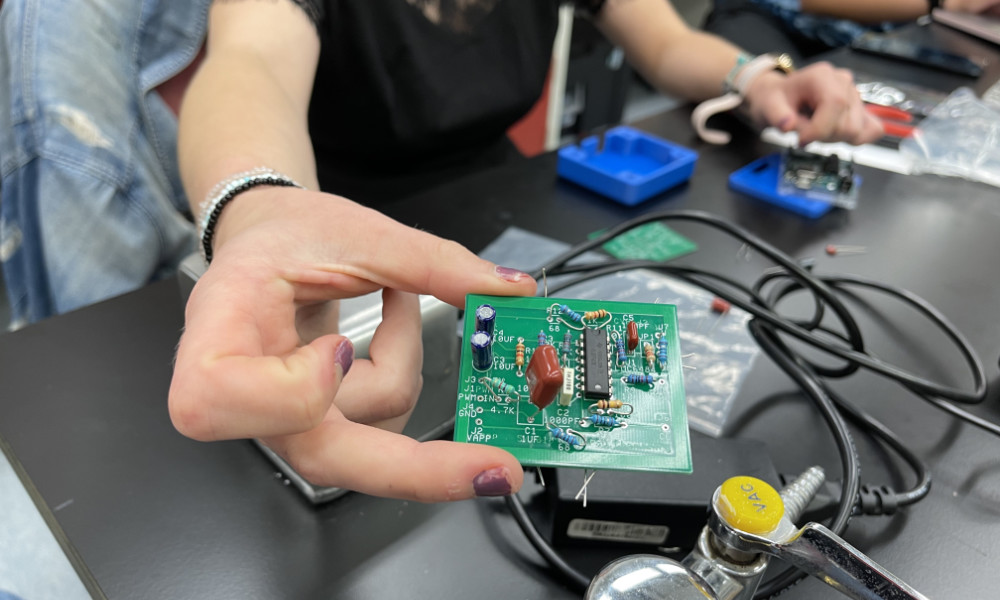
Rochester students’ award-winning device instantly detects sepsis via sweat
Rochester undergraduates have developed a fast, noninvasive, affordable, and eco-friendly way to diagnose the life-threatening medical complication.
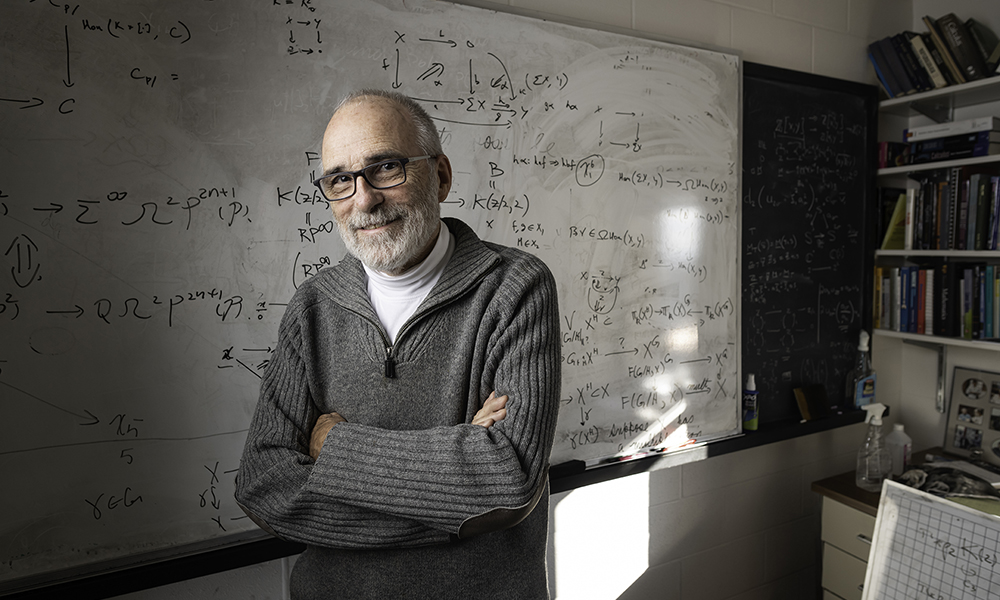

Rochester mathematician wins prestigious Veblen Prize
Fayerweather Professor of Mathematic Doug Ravenel wins the prize from the American Mathematical Society for solving a geometry problem that has puzzled mathematicians for 50 years.
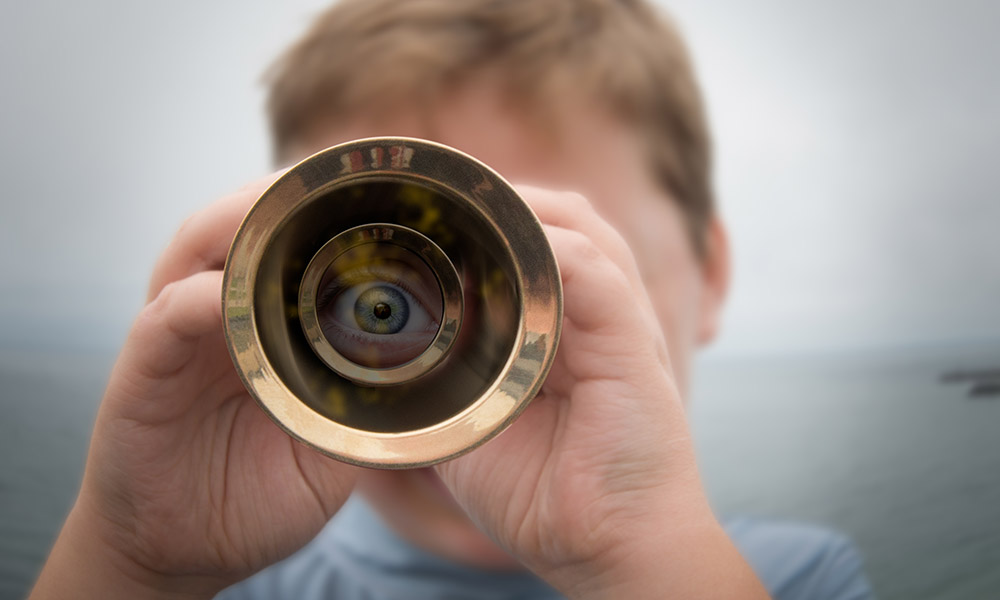

Brief period of ‘blindness’ is essential for vision
Rochester vision scientists uncover new information about the role of tiny “fixational” eye movements in enabling us to see clearly.
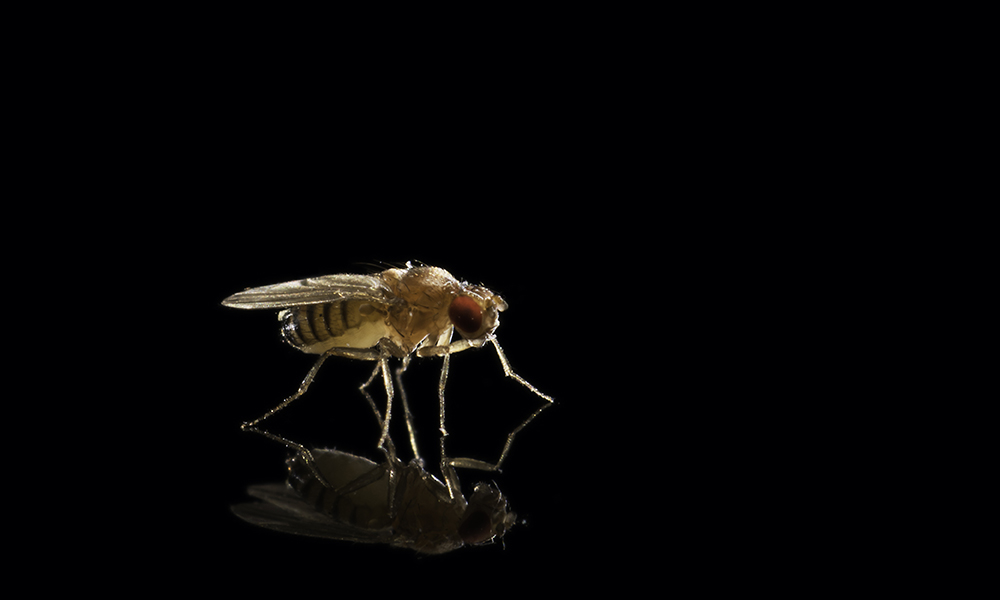

More evidence of an evolutionary ‘arms race’ between genes and selfish genetic elements
Christina Muirhead, a computational biologist and population geneticist in the lab of Daven Presgraves, further proves genes develop weapons to combat ‘parasites’ that litter the human genome.
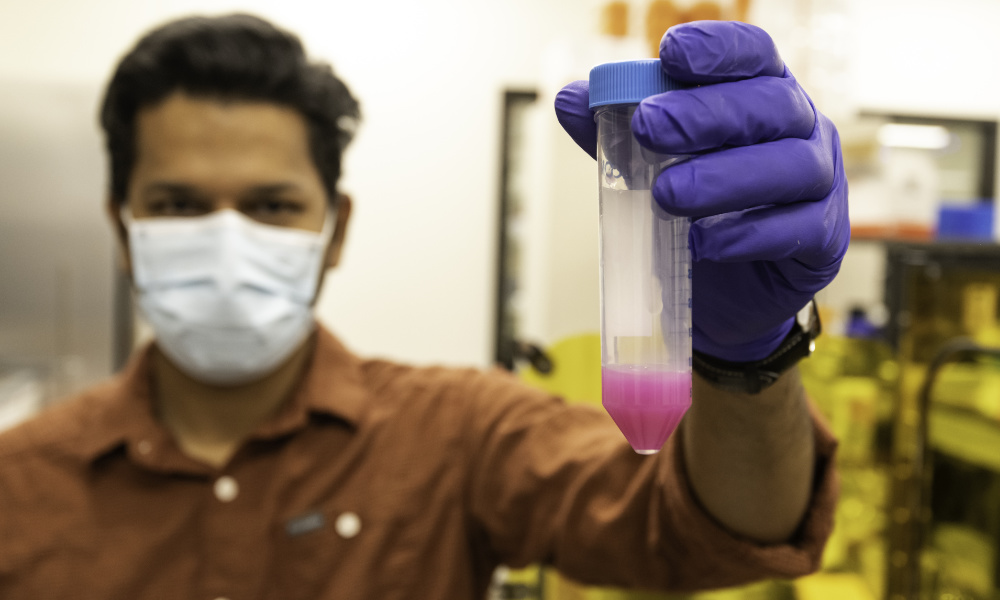

Researchers develop novel 3D printing technique to engineer biofilms
University of Rochester biologist Anne S. Meyer and her colleagues are studying how engineered biofilms closely mimic natural ones. Their research may aid in developing drugs to fight the negative effects of these microorganisms that adhere to surfaces.

Better models of atmospheric ‘detergent’ can help predict climate change
New research from Rochester scientist Lee Murray will aid in building more accurate computer models of the hydroxyl radical, an important ‘detergent of the atmosphere.’
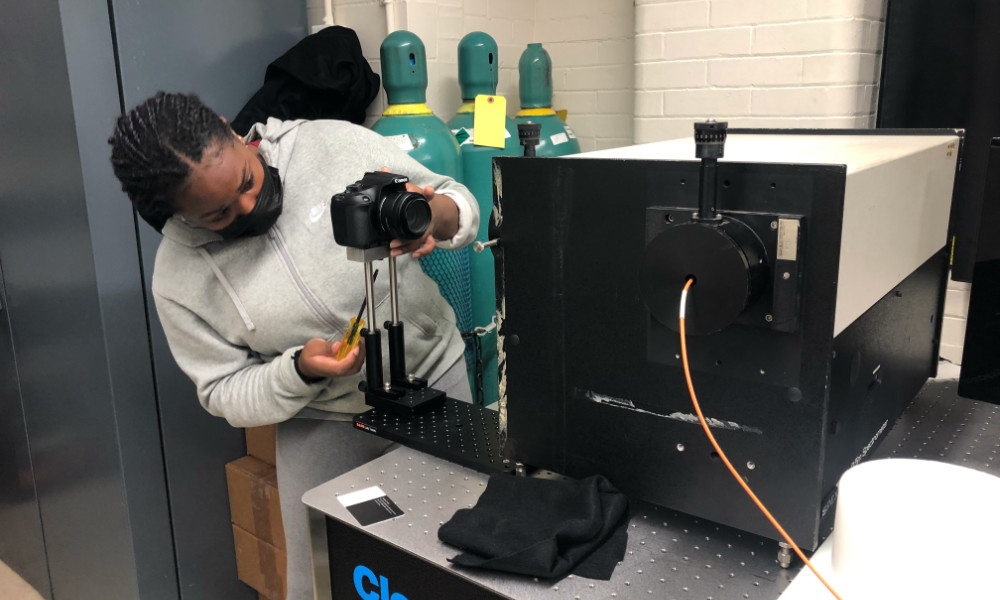

Future physicists experience research firsthand during internship at Rochester
The University of Rochester’s Center for Matter at Atomic Pressures (CMAP) hosted a five-week internship program this summer for area high school students to learn about high-energy-density physics, perform lab experiments, and work on projects with Rochester physics and astronomy graduate students.

