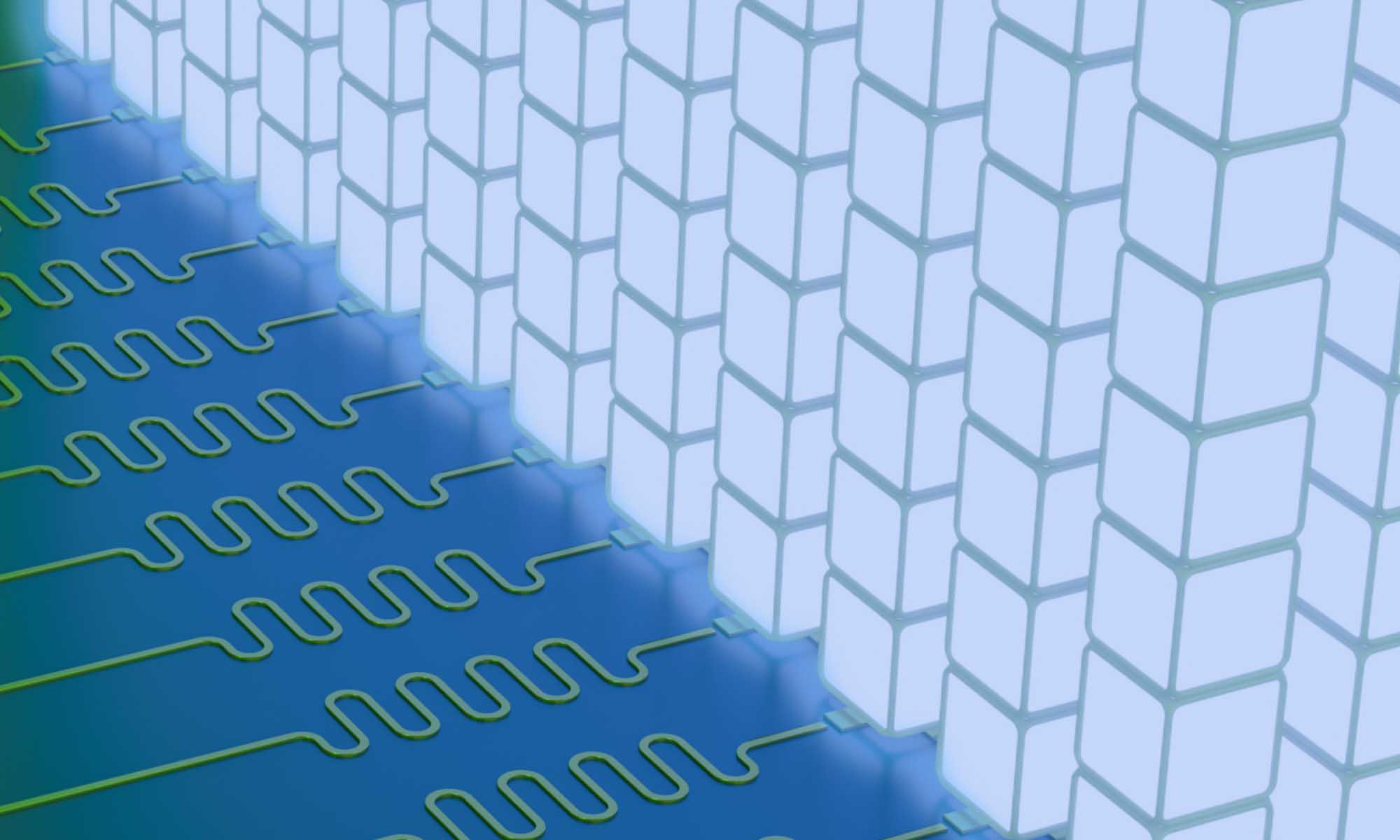
Researchers discover more efficient way to route information in quantum computers
Using qudits, Rochester scientists have solved a notoriously difficult problem involving Hilbert space, or the quantum matrix.
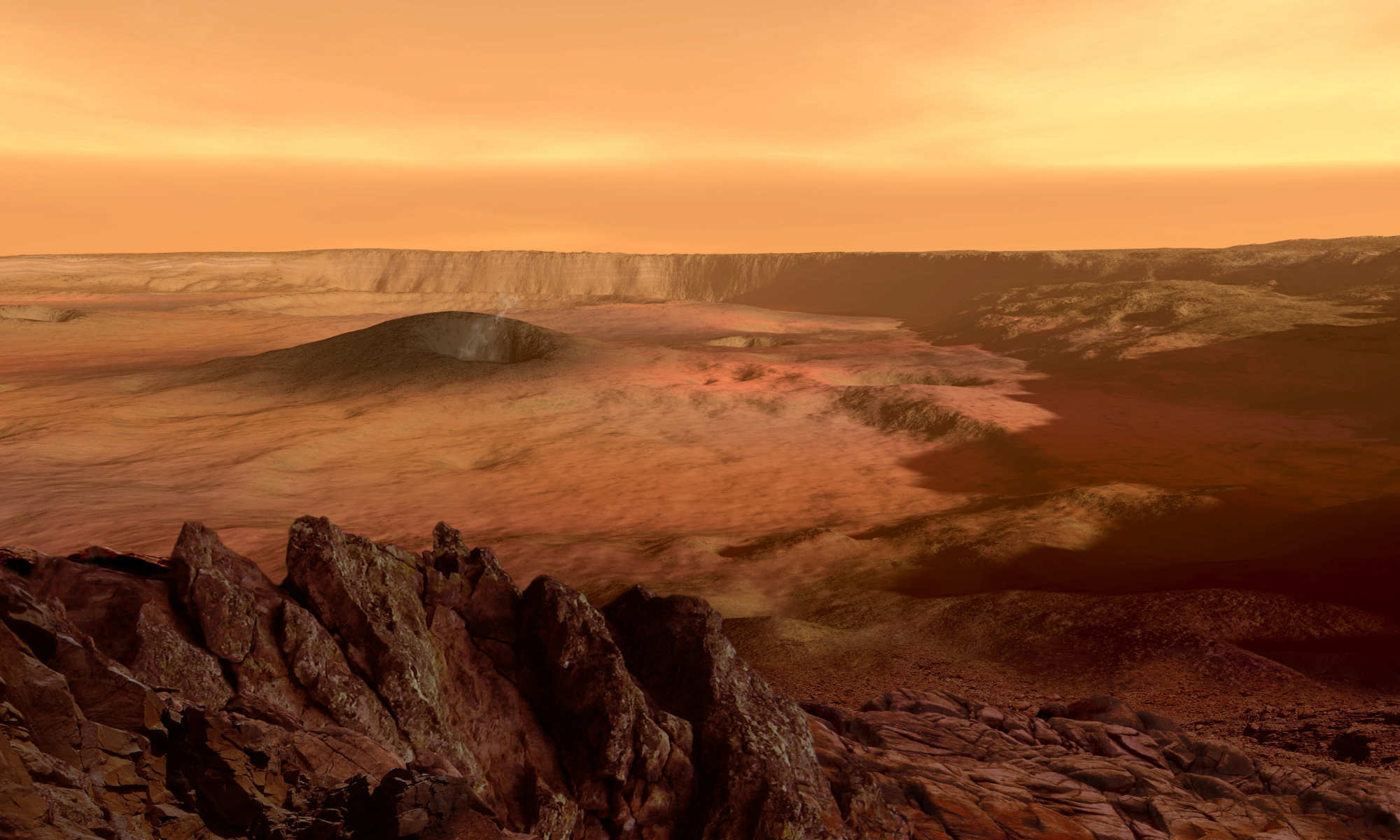

Mars surface patterns resemble Earth, revealing secrets of its past
Wave-like landforms on Mars offer insights about the planet’s icy past, its potential habitability, and the physics of flowing granular materials.
New molecule could pave the way for more efficient computers
A team of scientists has developed the “world’s most electrically conductive organic molecule.”

Bryce Davis ’20: Combining music and finance into a fulfilling career
The economics and music major found his path by embracing unexpected opportunities.
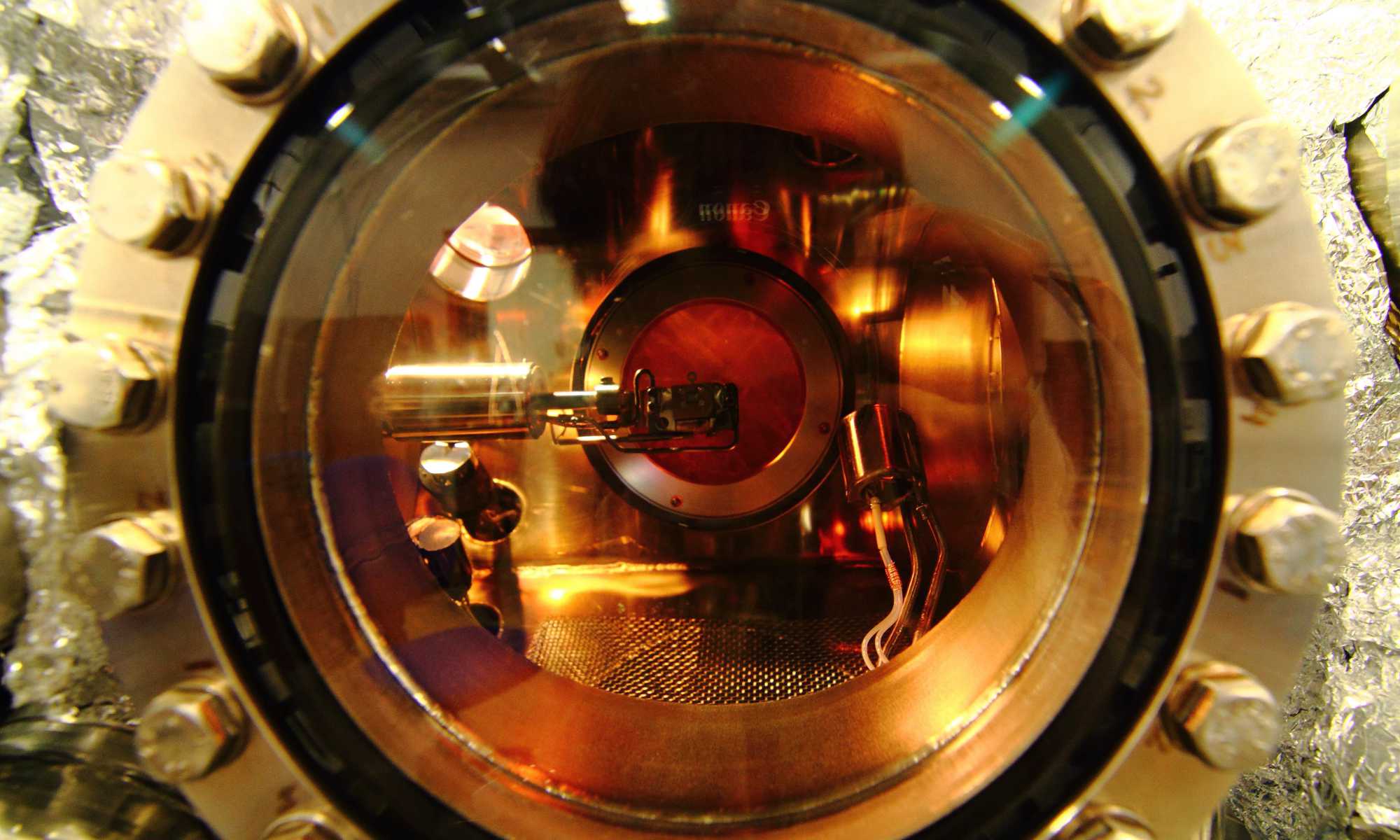
Scientists directly prove the existence of a nuclear-spin dark state
Confirmation of this elusive state in quantum systems could lead to more efficient quantum devices.

How Neanderthal DNA influenced human survival
New research provides an updated timeline of human-Neanderthal interactions, revealing patterns in the genetic legacy of this ancient exchange.
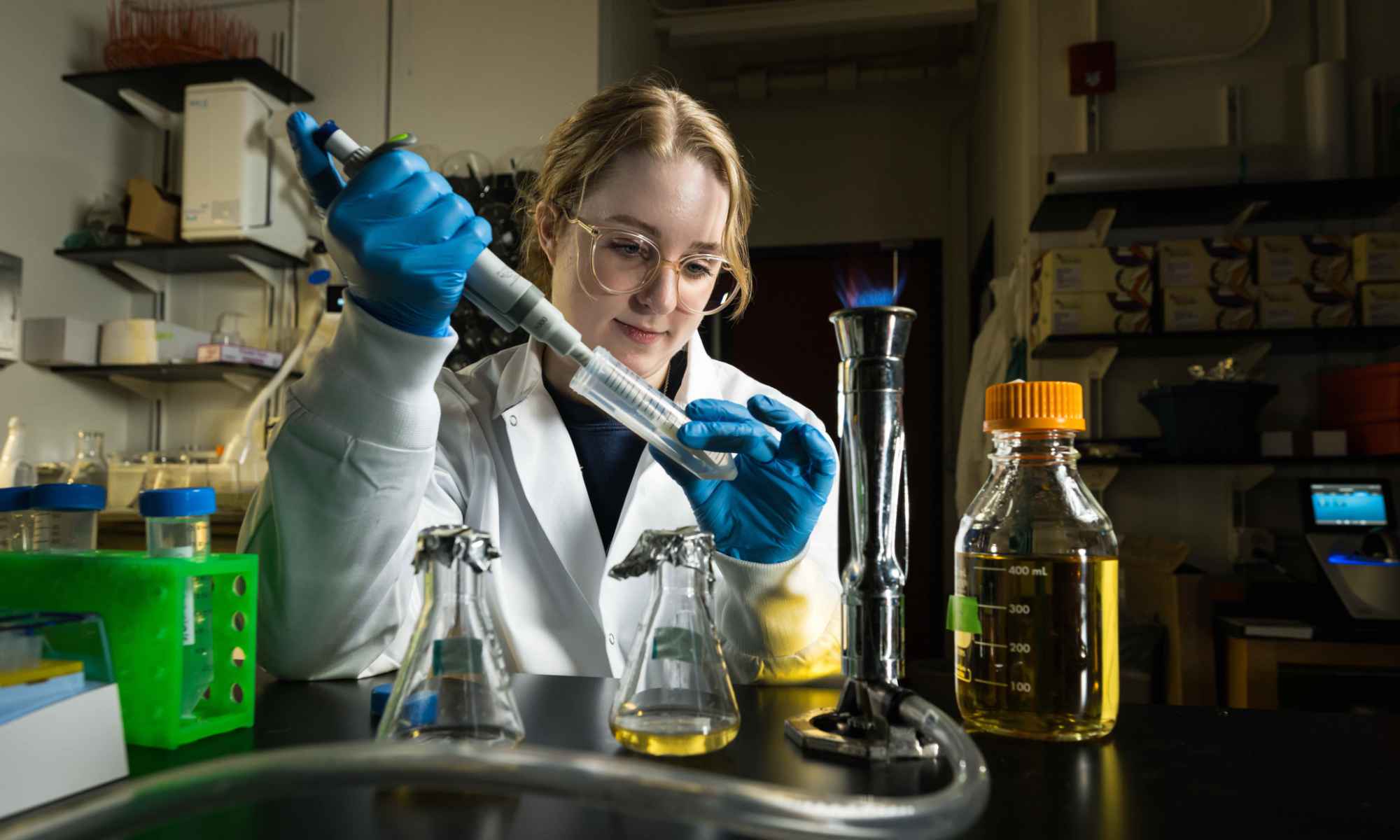

Can sea sponge biology transform imaging technology?
Researchers draw inspiration from nature to create tiny, powerful microlenses for advanced image sensors.
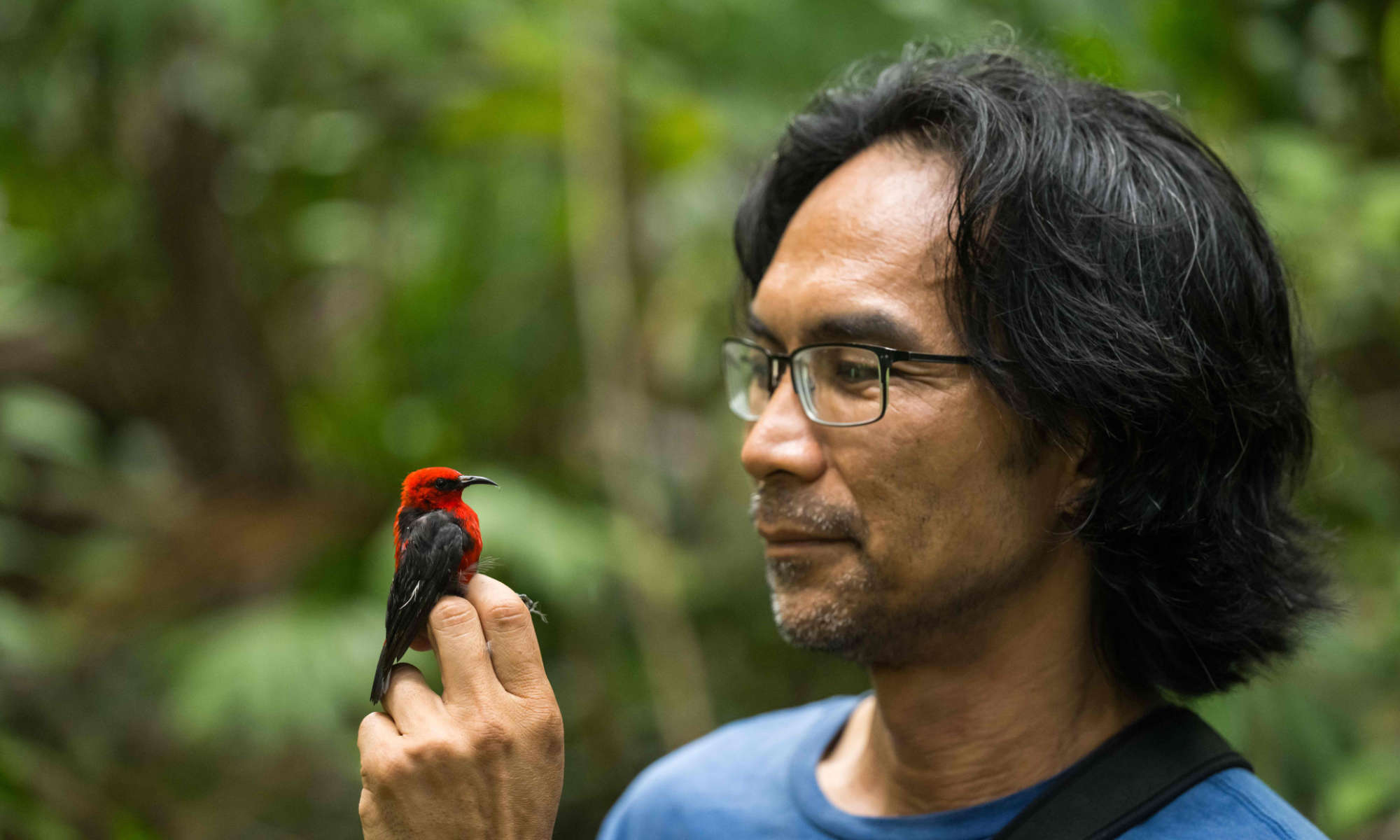

Evolution’s moment of truth
Every year biologist Al Uy travels by plane, boat, and foot to remote corners of the South Pacific to answer one of evolution’s biggest mysteries: How do species originate?
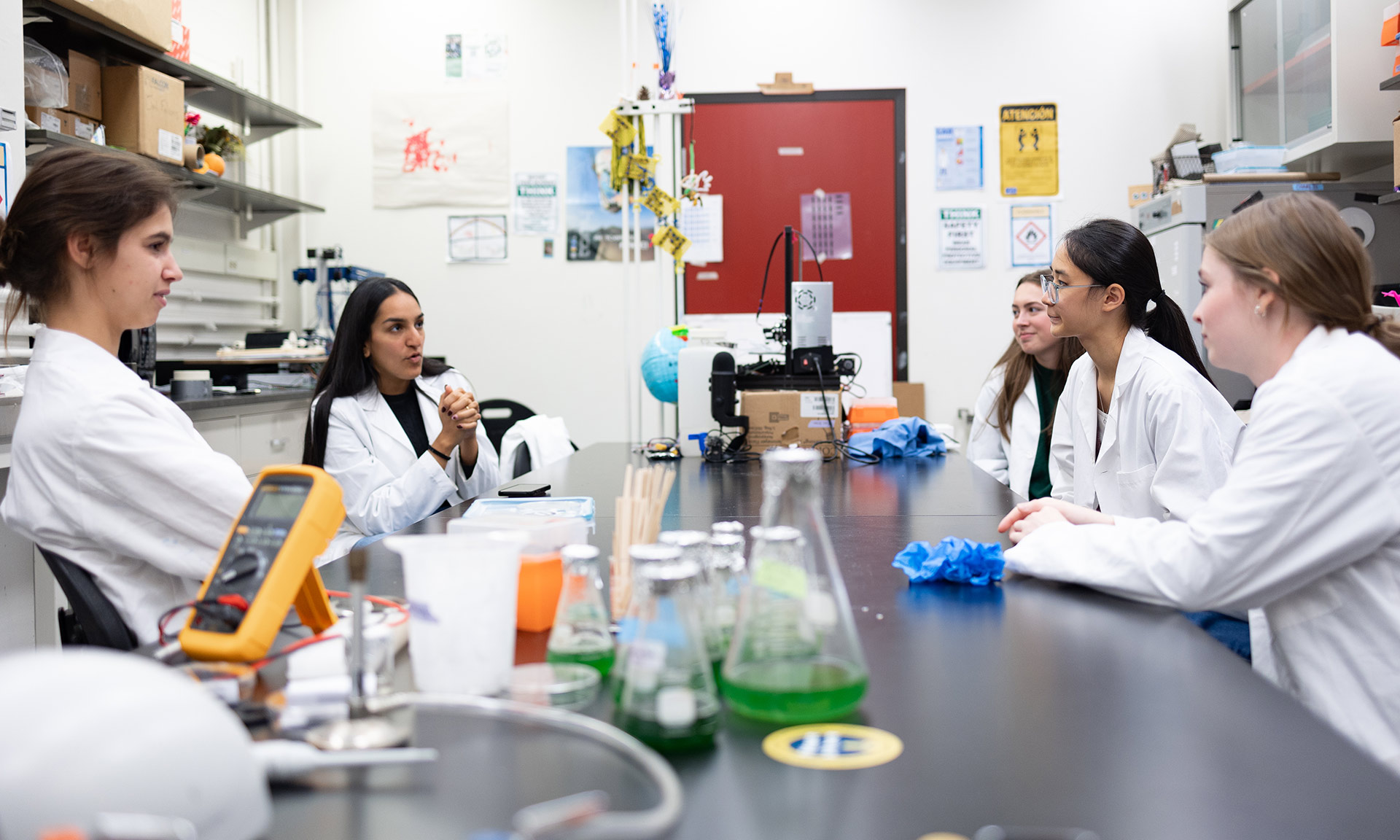

Undergraduate students use bacteria to create clean energy
The student-led team used synthetic biology to harness clean energy from bacteria while simultaneously capturing and storing carbon dioxide, taking home a gold medal in the process.

Why teens with autism struggle with speech intonation
A new study reveals that difficulties in adapting to changes in speech patterns may affect how adolescents with autism understand tone and meaning.

