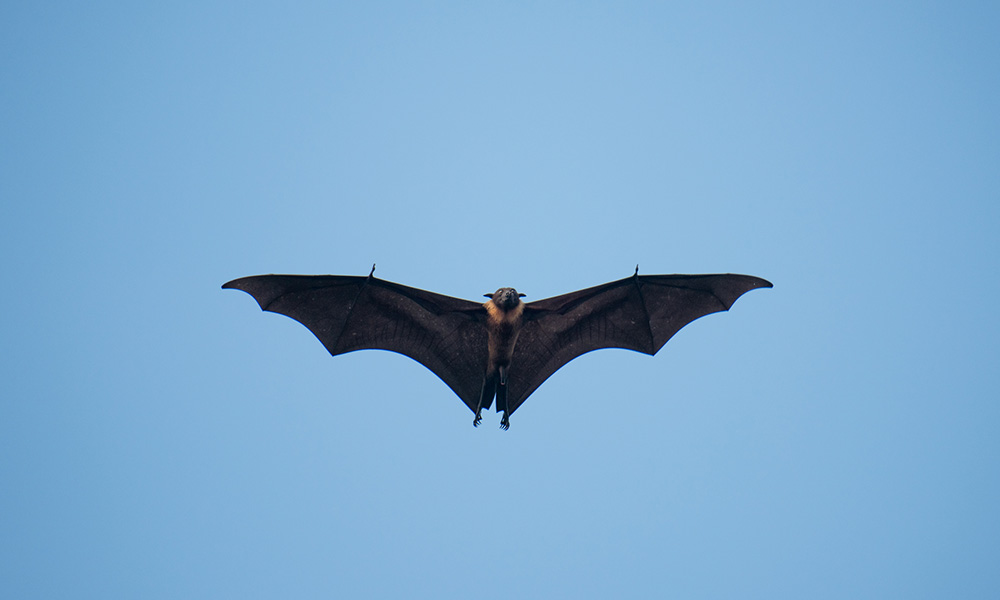

Bats offer clues to treating COVID-19
Bats carry many viruses, including the one behind COVID-19, without becoming ill. University of Rochester biologists are studying the immune system of bats to find potential ways to “mimic” that system in humans.
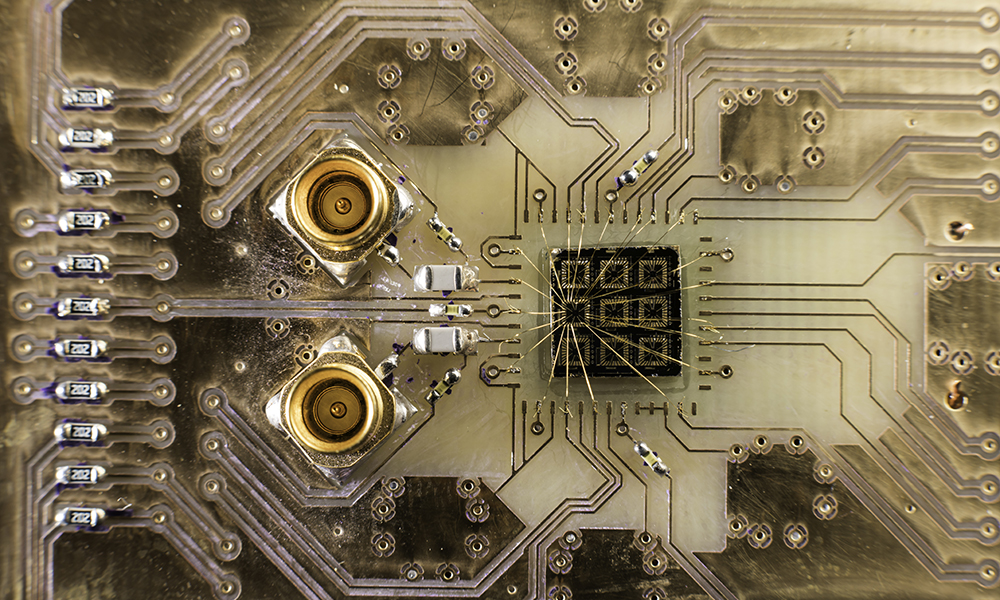
Is teleportation possible? Yes, in the quantum world
Rochester physicists are exploring new ways of creating quantum-mechanical interactions between distant electrons. The research marks an important advance in quantum computing.
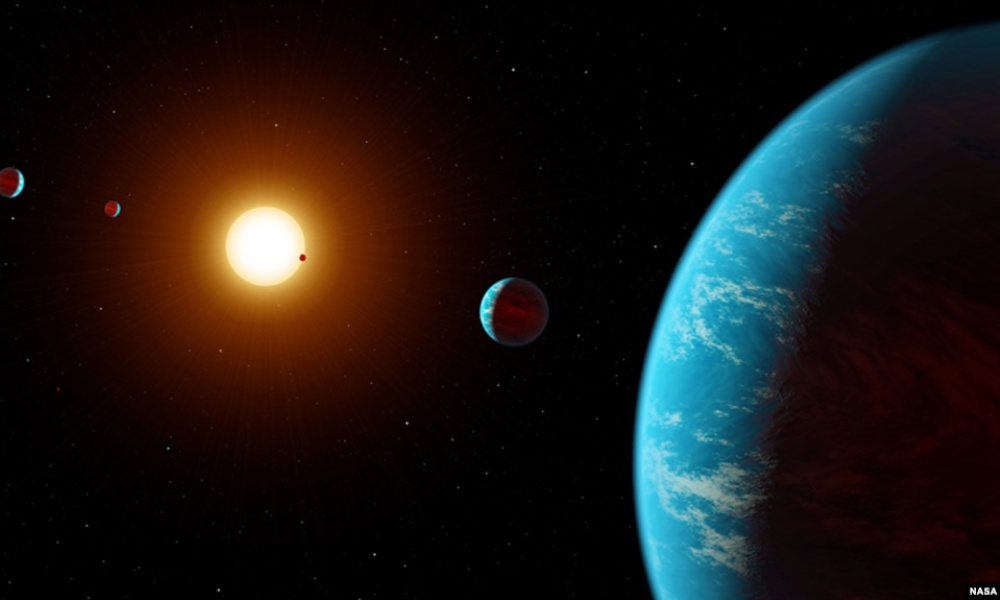

Are aliens real? Do aliens exist? Technosignatures may hold new clues
Astrophysicist Adam Frank is searching for “technosignatures,” or the physical and chemical traces of advanced civilizations, among the 4,000 or so exoplanets scientists have found so far.
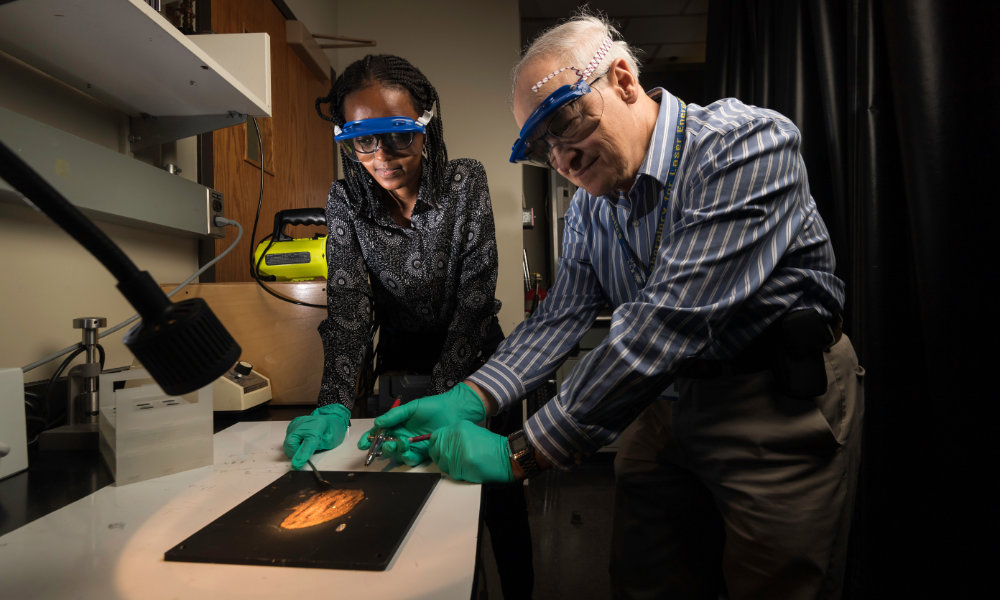

Laser Lab accepted into American Physical Society’s Inclusion, Diversity, and Equity Alliance
The University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics has joined the American Physical Society’s IDEA initiative, a new program to increase workforce diversity in physics departments and laboratories.

Study: Neurons can shift how they process information about motion
New Rochester research indicates some neurons can shift to process information about movement depending on the brain’s current frame of reference.

How Dr. Chat Bot evolved into a regionwide COVID-19 tracking tool
Members of an innovative technology and mobile applications lab at the Medical Center worked overtime to develop a state-of-the-art tool to help monitor the spread of coronavirus.
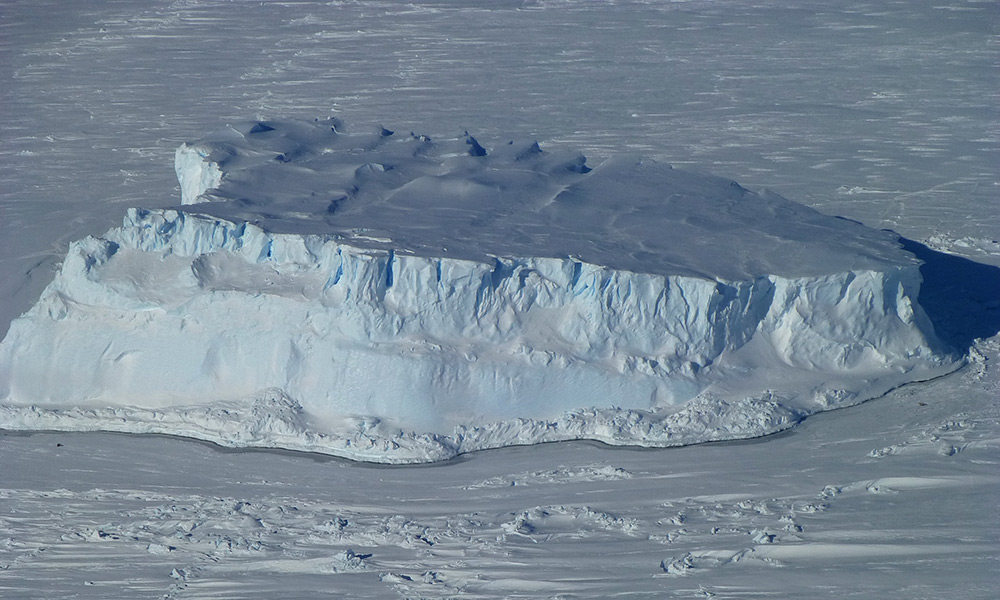

Rochester researchers unlock clues to a dramatic chapter of Earth’s geological history
New Rochester research indicates that the global glaciation period known as Snowball Earth began earlier than previously thought, work that adds to the understanding of how the planet’s climate changes.
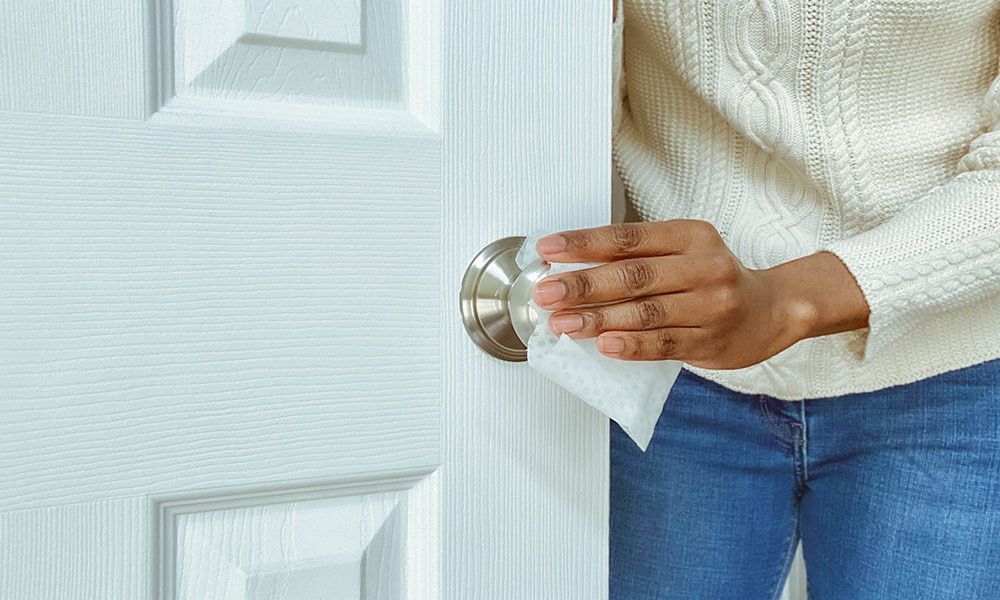

How to clean and disinfect—the right way
As businesses and other aspects of the economy open up, xxperts at the Medical Center offer tips for how to clean and disinfect your home during the COVID-19 pandemic.
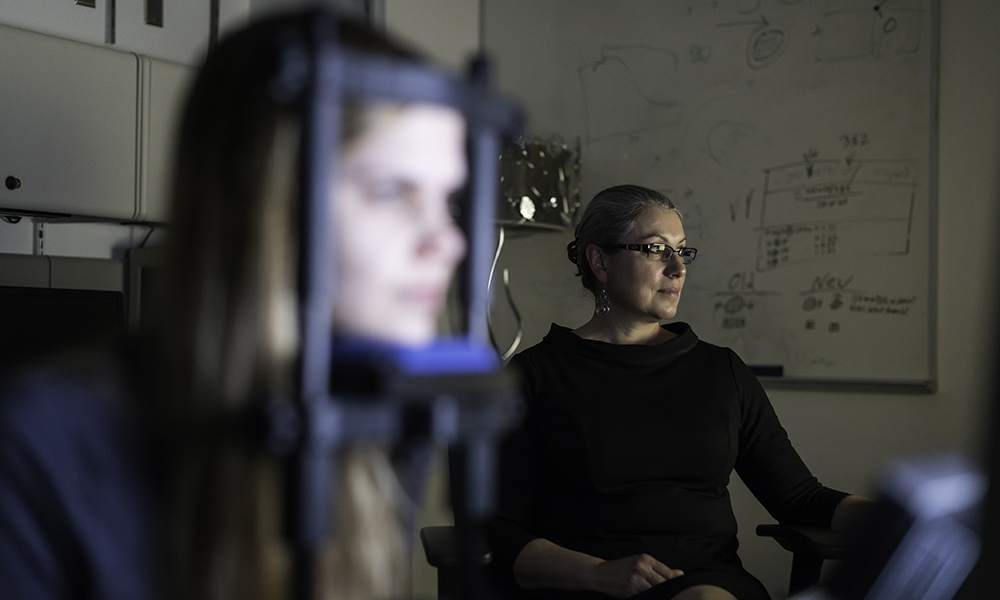

‘Time is vision’ after a stroke
A person who has a stroke that causes vision loss is often told there is nothing they can do to improve or regain the vision they have lost. A new study offers hope for stroke patients who have suffered vision loss—provided their treatment begins early.
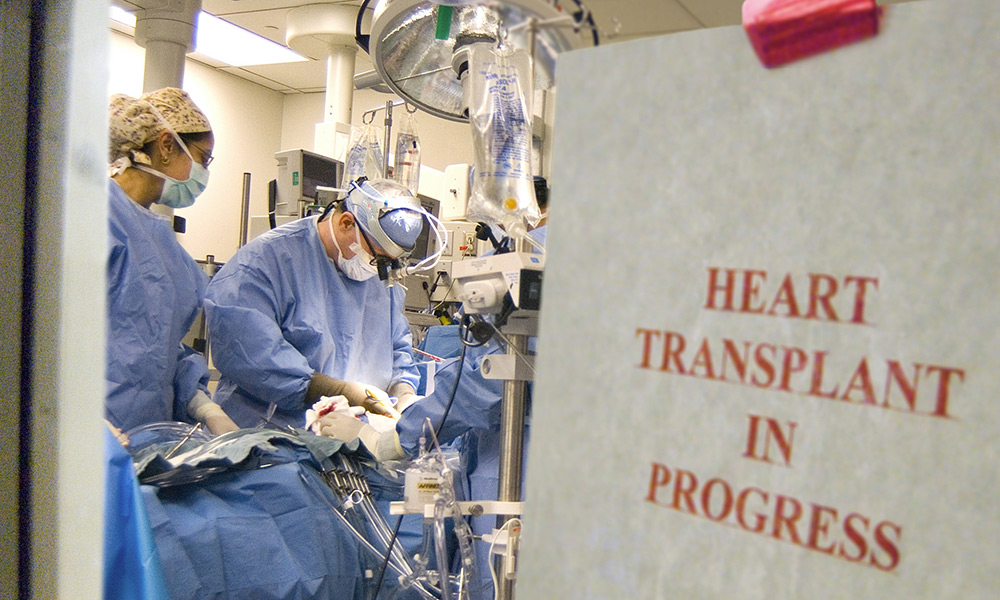
Organ transplant programs continue despite pandemic
Strong Memorial Hospital reaches a milestone as organ transplant surgeries continue to take place during the COVID-19 pandemic.
