Science & Technology
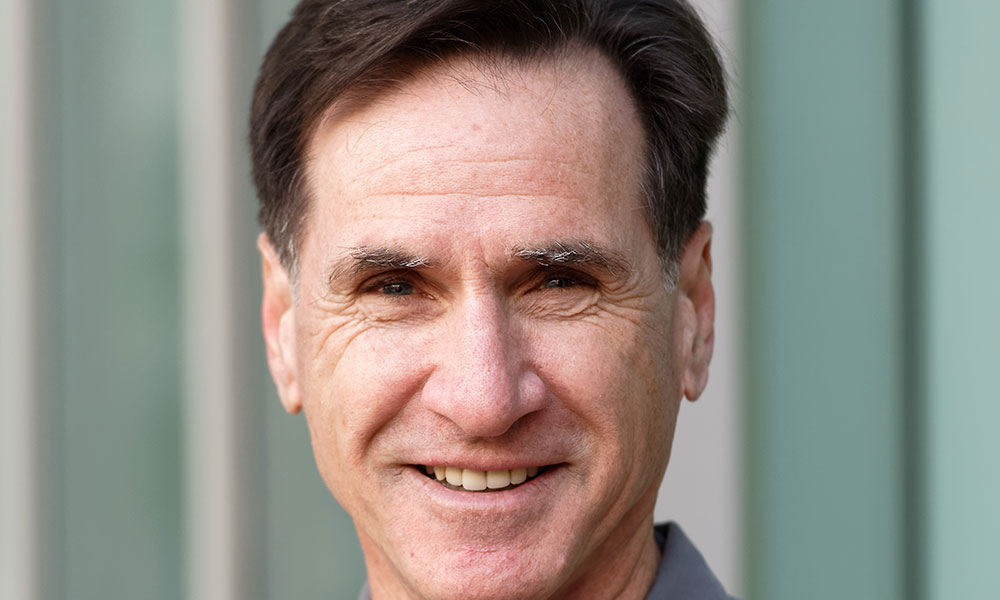
Q&A: Biologist earns raves for work with yeast
March 16, 2016
LISTEN: David Goldfarb, professor of biology, researches yeast as a model organism for understanding the aging process in humans. Why does this essential ingredient in bread and beer make a good research specimen?