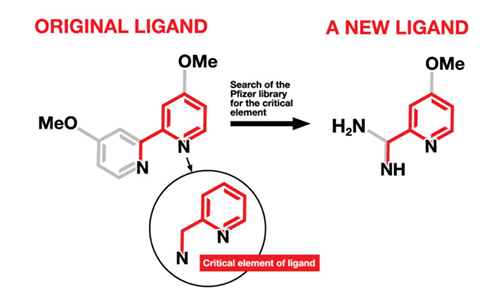
Finding needles in chemical haystacks
Chemists have developed a process for identifying new catalysts that will help synthesize drugs more efficiently and more cheaply, by searching libraries for drugs with structure features similar to known catalysts.
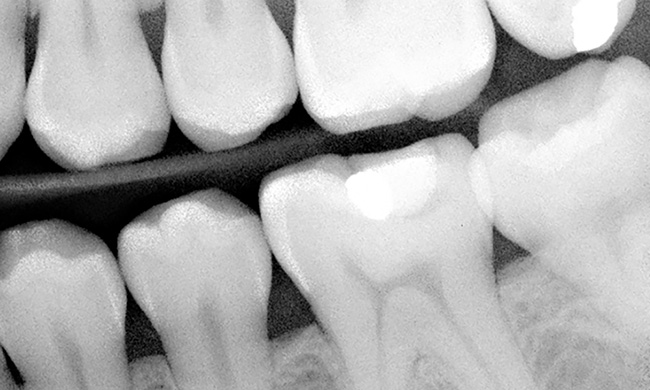
Nanoparticles provide novel way to apply drugs to dental plaque
Therapeutic anti-bacterial agents intended to reduce dental plaque and prevent tooth decay are often removed by saliva and the act of swallowing before they can take effect. But a team of researchers has developed a way to keep the drugs from being washed away.
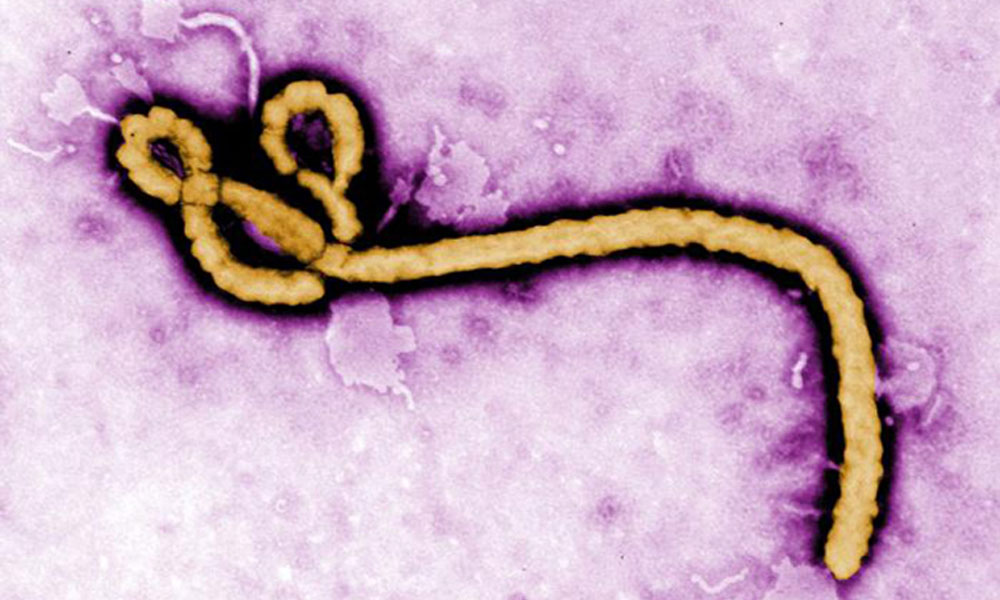
Ebola Q&A: Rochester researchers share their views
Given the widespread attention regarding the current Ebola outbreak in West Africa, four Medical Center faculty with expertise in viral infections field questions about the outbreak, the nature of pandemics, vaccines, and what a U.S. outbreak might look like.
Fund taps promising new technologies
UR Ventures has awarded three new Technology Development Fund (TDF) grants to projects in the fields of infectious disease, diabetes, and neuromedicine. Paul Dunman, Ph.D., with the Department of Microbiology…

UHS to attempt 5,000 flu vaccines in one day
On Thursday, Oct. 30, University Health Service (UHS) staff will attempt to vaccinate 5,000 students, faculty and staff against this year’s flu virus. The effort will doubly serve as a test of emergency preparedness to practice delivering mass quantities of vaccine or drug in response to an urgent public health concern. All River Campus-based students, faculty and staff are asked to consider participating in this clinic if they wish to receive the flu shot this year.
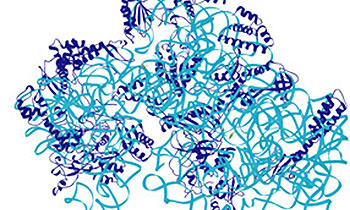
Targeting cells’ protein-making machinery may stop harmful bacteria
For the first time, the middle-steps in the process that creates the protein-making machinery of bacterial cells—called the ribosomes—has been isolated. A new study by biologist Gloria Culver suggests that blocking these pathways may help kill off drug-resistant bacteria.
Superbugs May Have a Soft Spot
Researchers have identified a weakness in at least one antibiotic-resistant superbug that scientists may be able to medically exploit.
