Science & Technology
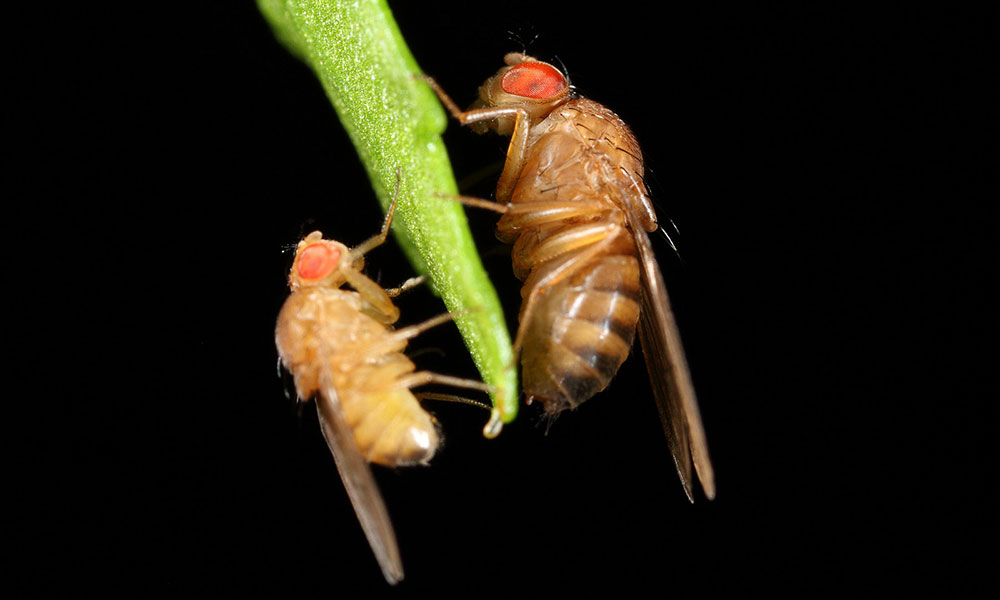
Fruit flies offer gut check on bacteria
April 26, 2017
Drosophila melanogaster—the common fruit fly—is widely used in laboratory experiments. But what Rochester researchers found when examining the guts of fruit flies in the wild bears little resemblance to what is seen in the lab.